 Getting Pregnant After 30
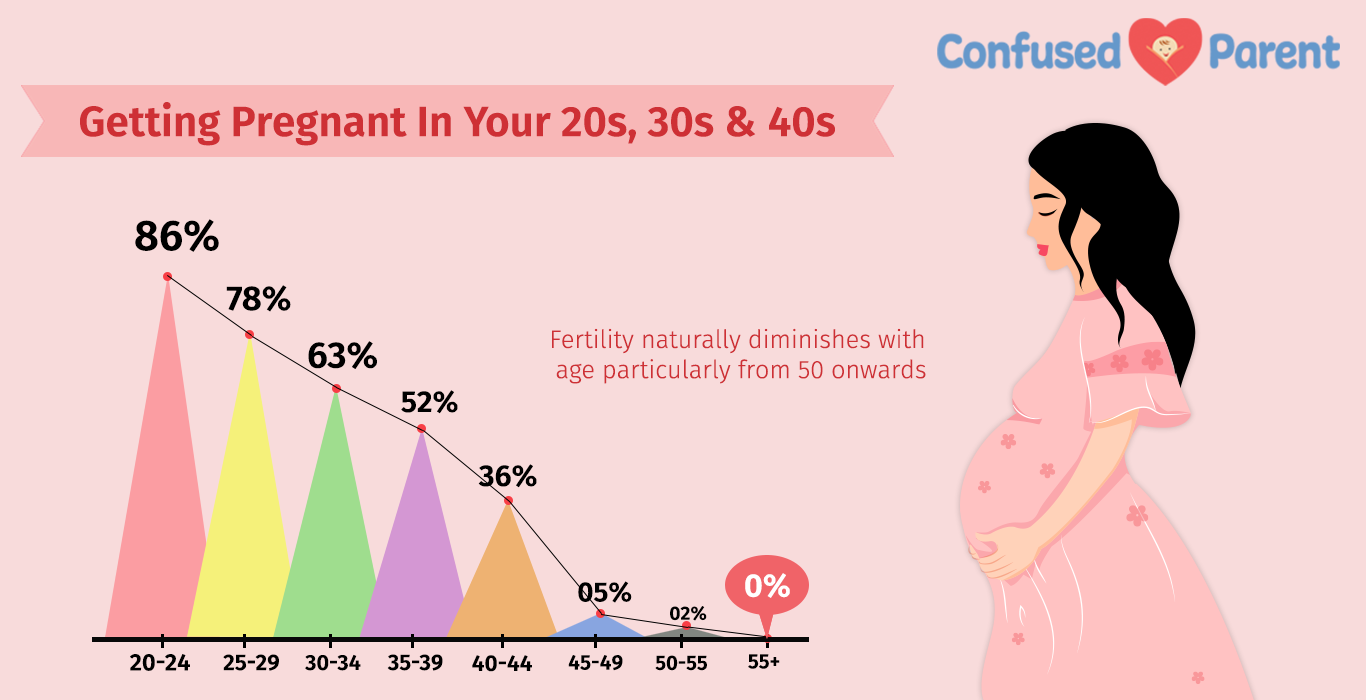
Getting Pregnant After 30peak reproductive years of a woman between the late teens and late 20s. At age 30, fertility (ability to conceive) began to decline. This decrease becomes faster once you reach your mid-30s. At age 45, fertility decreases thus getting pregnant naturally impossible for most women.
For healthy couples in their 20s and early 30s, about 1 in 4 women will become pregnant in any single menstrual cycle. At the age of 40 years, about 1 in 10 women will get pregnant per menstrual cycle. a man's fertility also declines with age, but is not suspected as a woman's fertility.
Women become less fertile as they age they start life with a fixed number of eggs in their ovaries. The number of eggs decreases as women get older. Also, the remaining eggs in older women are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities. And with increasing age, women are at a higher risk of disorders that can affect fertility, such as uterine fibroids and endometriosis.
Women who become pregnant in their 30s or 40s have a higher risk of complications. Some of these issues may affect women's health. Others can affect the health of the fetus.
Pregnant women older than 40 years have an increased risk of preeclampsia. Some of the increased risk may be due to older women tend to have more health problems before they become pregnant than younger women. For example, have high blood pressure, a condition that becomes more common with age, can increase the risk of preeclampsia. The study also showed that older women who do not have a health condition they may complicate pregnancy.
The overall risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities small. But as a woman ages, her risk of having a baby with missing, broken, or extra chromosomes increases. Down syndrome is the most common chromosome problems that occur later in childbirth. The risk of having a baby with Down syndrome
Yes. Prenatal screening tests assessing the risk that a baby will be born with certain birth defects or genetic disorders. prenatal diagnostic test can detect if the fetus has certain birth defects or genetic disorders. Every woman should review the testing options available to her obstetrician-gynecologist (ob-gyn) or other health care professional so that he can make an informed choice.
The risk of miscarriage and stillbirth is greater in women older than 35 years. Also, multiple pregnancies are more common in older women than in younger women. As ovaries age, they are more likely to release more than one egg per month.
All of the women have to think about whether they want to have children and, if so, when to have them. This is called a reproductive life plan. If you would like to have children someday, your ob-gyn or health care professional can help you develop a plan other of your reproductive life.
It is a good idea to talk about your plans once a year with your ob -gyn or other health care professional.
If you do not want to become pregnant now or have decided not to have children, using birth control methods to prevent pregnancy if you have sex. Make sure you use the method that suits your purpose of reproduction, your lifestyle, and health conditions you have. You and ob-gyn or other health care professional can review your birth control options.
If you want to get pregnant soon, you should try to be as healthy as possible before pregnancy. Steps toward better health, including stopping alcohol, tobacco and cannabis use. You also have to start taking folic acid to help prevent neural tube defects.
The visit health care before pregnancy is the time to ob-gyn or other health care professional to review your medical history and your family. He will also review the medications you take and your immunization to ensure that you have all the recommended vaccines. Your ob-gyn or other health professionals also can
Currently, there are no medical technique that can guarantee the fertility will be maintained. If you know that you want to have children later in life, the choice might in vitro fertilization (IVF). With IVF, the sperm is combined with the female egg in the laboratory. If the sperm fertilizes the egg, the embryo can grow. Embryos can be frozen and used for many years later. When you are ready, the embryos can be transferred to your uterus to try to achieve pregnancy.
It's likely that IVF will work for you depends on the peds on many factors, including your health and your age when the embryos were frozen. Speaking at a fertility expert will help you understand your chances of success with IVF.
Some of the IVF treatments are expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
In a procedure called oocyte cryopreservation- "freezing your eggs" -Some eggs released from the ovary. Unfertilized egg is then frozen for use in IVF. Egg freezing is recommended especially for women having cancer treatment that will affect their future fertility. There is not enough research to recommend egg freezing routine for the sole purpose of delaying childbirth. Egg freezing is also expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
If you are older than 35 years and have not become pregnant after six months of regular sexual intercourse without using a form of birth control, talk to your ob-gyn or other health care professional about infertility evaluation. If you are older than 40 years, the evaluation is recommended before trying to conceive. This advice is especially true if you have a problem that can affect fertility, such as endometriosis.
During the infertility evaluation, you have a physical exam and tests to try to find the cause of infertility. If the cause is found, treatment may be possible. In many cases, infertility can be successfully treated even if no cause is found. But the chances of success with this treatment decreases with age.
Yes. Despite the challenges, many women older than 35 years can have a healthy pregnancy and baby. See your health care professional before pregnancy and receive good prenatal care during pregnancy is key.
When you are pregnant, getting early and regular prenatal care can increase your chances of having a healthy baby. You should visit your ob-gyn or other health care professional regularly. At each visit, your health and your baby's health will be monitored. If you have a medical condition that already exists or if a medical condition develops during pregnancy, you may need to have special tests or more frequent prenatal care visits. You may also need special care during labor and delivery
Carrier Screening :. A test performed on someone with no signs or symptoms to know if she carries the gene for a genetic disorder.
Chromosome: Structure located in every cell in the body and contains genes that determine a person's physical composition
Diagnostics Test :. Tests that look for a disease or cause the disease
Down Syndrome :. A genetic disorder that causes abnormal facial features and body, medical problems such as heart defects and intellectual disabilities. Most cases of Down syndrome is caused by an extra chromosome 21 (trisomy 21). Many children with Down syndrome live into adulthood
Embryo: .. stage of prenatal development begins at fertilization (joining of egg and sperm) and lasts up to 8 weeks
Endometriosis: A a condition in which the tissue lining the uterus is found outside the uterus, usually on the ovaries, fallopian tubes and other pelvic structures
Fetus :. stage of prenatal development that started 8 weeks after conception and lasts until the end of pregnancy
Fibroids :. Growth, usually benign, that forms the uterine muscle
Folic Acid :. A vitamin that has been shown to reduce the risk of certain birth defects when taken in sufficient quantities before and during pregnancy
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). A procedure in which eggs removed from the woman's ovaries, fertilized with sperm in the laboratory, and then transferred into the woman's uterus to achieve pregnancy
Miscarriage: .. Losing pregnancy
Neural Tube Defects s : the birth defects that result from incomplete development of the brain, spinal cord, or their coverings
Obstetrics-Gynecology (Ob-Gyn) :. A doctor with specialized skills, training, education and women's health.
oocytes Cryopreservation: A procedure in which eggs are removed from a woman's ovaries and frozen for later use with in vitro fertilization
Ovarian :. The paired organ in the female reproductive system containing eggs released at ovulation and produce hormones
Preeclampsia :. A disorder that can occur during pregnancy or after childbirth in which there is high blood pressure and other signs of organ injury, such as an abnormal amount of protein in the urine, a lower number of platelets, abnormal kidney or liver function during upper abdominal pain, fluid in the lungs, or severe headaches or changes in vision
Prenatal Care :. A treatment program for pregnant women before the birth of her baby
Screening Test :. Tests that look for possible signs of the disease in people who have no signs or symptoms
Sexual Intercourse :. the actions of the male penis enters the vagina (also referred to as "sex" or "fuck")
sexually transmitted infections (STIs). An infection that is spread through sexual contact, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes, syphilis, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV, the cause of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [AIDS])
stillborn .. Birth dead fetus
the uterus: a muscular organ located in the female pelvis that contains and maintains the developing fetus during pregnancy
FAQ060 :. This information is designed as an educational aid for patients and sets forth current information and opinions related to women's health. It is not intended as a statement of the standard of care, is not made up of all the appropriate care or treatment methods. It is not a substitute for independent professional assessment of this treating clinician. Please check for updates on to ensure accuracy.
Copyright July 2018 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
FAQs Related
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 409 12th Street SW, Washington, DC 20024-2188 Mailing Address: PO Box 96920, Washington, DC 20024-9998
 Pregnancy After 30: The Health Affects of Having a Baby Later in Life
Pregnancy After 30: The Health Affects of Having a Baby Later in Life Can pregnancy after 30 have health benefits? | health enews
Can pregnancy after 30 have health benefits? | health enews Pregnancy After Age 35 and Pregnancy at the Age 45 and After 45 ...
Pregnancy After Age 35 and Pregnancy at the Age 45 and After 45 ... How to Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 ...
How to Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 ... How to increase your chances of pregnancy after 30 - Health - The ...
How to increase your chances of pregnancy after 30 - Health - The ... Pregnancy after 30 - dangerous for mother and baby ...
Pregnancy after 30 - dangerous for mother and baby ... The Pregnancy After 30 Workbook: Amazon.com: Books
The Pregnancy After 30 Workbook: Amazon.com: Books How to Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 Audi…
How to Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 Audi… What nobody tells you about getting pregnant after 30
What nobody tells you about getting pregnant after 30 How to Conceive Naturally and Have a Healthy Pregnancy After 30 ...
How to Conceive Naturally and Have a Healthy Pregnancy After 30 ...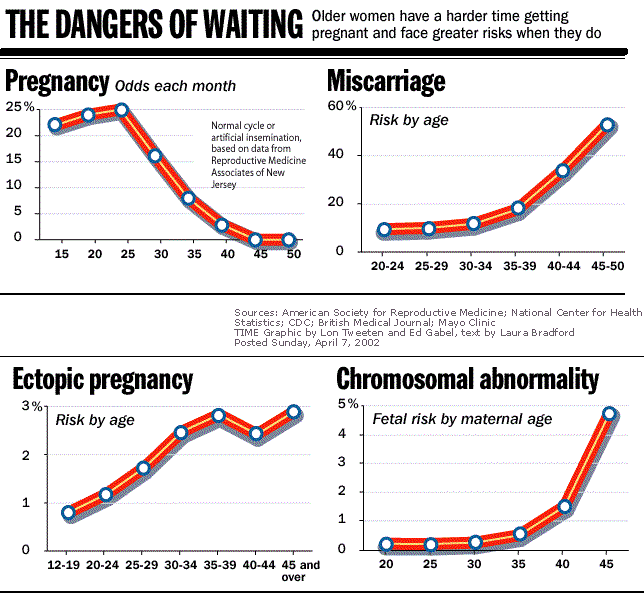 Getting Pregnant In Your 20s, 30s & 40s
Getting Pregnant In Your 20s, 30s & 40s 7 Pros And Cons Of Getting Pregnant In Your 30s
7 Pros And Cons Of Getting Pregnant In Your 30s Getting Pregnant After the Age of 30 & what you can do to boost ...
Getting Pregnant After the Age of 30 & what you can do to boost ... How to Conceive Naturally And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 Audio…
How to Conceive Naturally And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 Audio… Pregnancy: 30 Weeks
Pregnancy: 30 Weeks The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30: Carol Winkelman ...
The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30: Carol Winkelman ... How to Prepare for Pregnancy After 40: 13 Steps (with Pictures)
How to Prepare for Pregnancy After 40: 13 Steps (with Pictures) Pregnancy Risks After 30: From Low Fertility, Child Birth ...
Pregnancy Risks After 30: From Low Fertility, Child Birth ... How To Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 $Do…
How To Conceive Naturally: And Have a Healthy Pregnancy after 30 $Do… New Model Predicts Women's Odds Of Getting Pregnant | HuffPost
New Model Predicts Women's Odds Of Getting Pregnant | HuffPost Pregnancy after 30: Chances of Pregnancy and How to Prepare for It ...
Pregnancy after 30: Chances of Pregnancy and How to Prepare for It ... Getting pregnant after 30 — the only guide you need for a safe ...
Getting pregnant after 30 — the only guide you need for a safe ... The Pregnancy-After-30 Workbook: Program for Safe Childbearing, No ...
The Pregnancy-After-30 Workbook: Program for Safe Childbearing, No ... Pregnancy Risks After 30: From Low Fertility, Child Birth ...
Pregnancy Risks After 30: From Low Fertility, Child Birth ... How to help ensure a healthy pregnancy after 35 | Your Pregnancy ...
How to help ensure a healthy pregnancy after 35 | Your Pregnancy ... Frequently Used Fertility Statistics Are 300 Years Old And May Be ...
Frequently Used Fertility Statistics Are 300 Years Old And May Be ... Pregnancy after 30
Pregnancy after 30 Pregnant after 30: Dr. Seale Discusses Health Differences and ...
Pregnant after 30: Dr. Seale Discusses Health Differences and ... Advanced Maternal Age Pregnancies (Getting Pregnant After 35)
Advanced Maternal Age Pregnancies (Getting Pregnant After 35) Your Pregnancy after 30 by Curtis, Glade B. 9781555610883 | eBay
Your Pregnancy after 30 by Curtis, Glade B. 9781555610883 | eBay The Pregnancy-After-30 Workbook: A Program for Safe Childbearing ...
The Pregnancy-After-30 Workbook: A Program for Safe Childbearing ... Age and the Risk of Miscarriage | Expecting Science
Age and the Risk of Miscarriage | Expecting Science Faint lines after 30 mins. Plz help - BabyCenter
Faint lines after 30 mins. Plz help - BabyCenter Pin on Daily
Pin on Daily Babies after 30 : Health Risks of Mid Life Pregnancy - YouTube
Babies after 30 : Health Risks of Mid Life Pregnancy - YouTube Why The Average Age For Pregnancy Is Now In Your 30s – Vogue Hong Kong
Why The Average Age For Pregnancy Is Now In Your 30s – Vogue Hong Kong Pregnancy Complications After 30 – Bleeding During Pregnancy ...
Pregnancy Complications After 30 – Bleeding During Pregnancy ... Mother who had mastectomy 30 minutes after giving birth | Daily ...
Mother who had mastectomy 30 minutes after giving birth | Daily ...![Download eBook [PDF] The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30 Best Re… Download eBook [PDF] The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30 Best Re…](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/downloadebookpdfthecompleteguidetopregnancyafter30bestreview-191111014509-thumbnail-4.jpg?cb=1573436730) Download eBook [PDF] The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30 Best Re…
Download eBook [PDF] The Complete Guide to Pregnancy After 30 Best Re… FFP 061 | How to Conceive Naturally and Have a Healthy Pregnancy ...
FFP 061 | How to Conceive Naturally and Have a Healthy Pregnancy ... A Healthy Pregnancy After 30 - The Craving Shift
A Healthy Pregnancy After 30 - The Craving Shift Pregnancy on d 30 (A) and pregnancy on d 65 (B) after the first AI ...
Pregnancy on d 30 (A) and pregnancy on d 65 (B) after the first AI ... How To Get Pregnant Fast
How To Get Pregnant Fast Pregnancy after 30 by Tanvi aggerwal - issuu
Pregnancy after 30 by Tanvi aggerwal - issuu Probability of pregnancy on day 30 after timed artificial ...
Probability of pregnancy on day 30 after timed artificial ... Pregnancy after tummy tuck 30 weeks pregnant - YouTube
Pregnancy after tummy tuck 30 weeks pregnant - YouTube You can get pregnant, even after 30 or 40! The old statistics ...
You can get pregnant, even after 30 or 40! The old statistics ... Pregnancy After 30 | Pregnancy After 30
Pregnancy After 30 | Pregnancy After 30 Pregnancy after bypass: Week 30 pregnancy diary - Melissa Loses It
Pregnancy after bypass: Week 30 pregnancy diary - Melissa Loses It Positive Tests after 30 minutes, possible evap? - BabyCenter
Positive Tests after 30 minutes, possible evap? - BabyCenter
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar