:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ovarypainfinal-01-5be8f3e846e0fb0051ce313d.png) Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor
Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a DoctorThe ovary is an important part of. Their task is two-fold. They produce hormones, including, triggers it. They also released at least one egg each month for possible fertilization.
A number of different conditions, from the cyst tumor, can cause. Ovary located below. That means if you have ovarian pain, most likely you will feel it in your lower abdomen - below the navel - and pelvis. It is important to have inspected by your regular doctor or his / gynecologist. Several different conditions can cause it.
Pain in the ovaries can either be acute or chronic. Acute ovarian pain came quickly (for a few minutes or days) and lost in a short time. Ovarian chronic pain usually starts more gradually. Then last for several months or more.
ovarian pain may be continuous. Or may come and go. It may be worse with certain activities, such as or urination. It can be so mild that you do not realize it. Or pain in the ovary can be so severe that it interferes with daily life.
The method doctors use to diagnose ovarian pain will vary. They will be based on what is suspected as possible causes. Regardless, the doctor will take a complete medical history, conduct, and ask questions about your pain. Questions might include:
diagnostic tests, such as and other types of imaging, can zero in on the cause of the pain. Here is an overview of some of the possible causes of ovarian pain and how they are diagnosed and treated.
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on the ovaries. They are very common in women, especially during the childbearing years. Often they are formed during the process. This can occur when the egg is not released or when the sac - follicle - holding an egg does not dissolve after the egg is released. usually causes no symptoms and disperse on their own. They can, though, make the pain or sharp pain when a large cyst and ruptured.
Other symptoms of ovarian cysts:
How diagnosed ovarian cysts
Treatment of ovarian cysts
Tumors can form in the ovaries, such as those formed in other parts of the body. They can be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant).
Other symptoms of ovarian tumors
How ovarian tumors diagnosed
Treatment of ovarian tumors
Learn more about.
Each month, the lining of the uterus builds up in preparation to nourish the growing fetus. When the egg is not fertilized, that shed layers and released from the body through menstruation. In some women, the uterus lining develops networks like elsewhere in the body. This tissue swells and bleeds each month. It was a place to dump, though, and can form scar tissue that can be very painful.
Other
how it is diagnosed
treatment of endometriosis
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the ovaries, uterus or fallopian tubes. It is most often caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea or chlamydia. It is one of the most common causes of pelvic pain in women.
Other symptoms of PID
How is PID diagnosed
treatment of PID
Antibiotics. These drugs are given by mouth or by injection. They can kill the bacteria that cause PID. If you take antibiotics for PID, your sex partner or partners should also be treated. There is a high possibility that your partner has a sexually transmitted infection that is the same. Learn more about.
Surgery to remove the uterus and ovaries known as hysterectomy and oophorectomy. A salping- bilateral oophorectomy is a procedure in which both the fallopian tubes and ovaries are removed. In rare cases, a small piece of the ovary may be inadvertently left behind. the remainder can grow and develop painful cysts.
Other symptoms of residual ovarian syndrome
How the rest of diagnosed ovarian syndrome
Ultrasound, CT, and MRI. These scans create images of the area. They help doctors find leftover pieces of ovarian tissue.
Treatment of residual ovarian syndrome
Laparotomy or laparoscopy. This procedure is done to remove parts or pieces remaining ovary. Learn more about
SOURCE :.
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: "Endometriosis"
CDC: "Pelvic Inflammatory Disease."
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: "Pelvic Pain"
"Ovaries." Katz, VL, Lentz, GM, Lobo, RA, Gershenson, DM. Comprehensive Gynecology. 5th ed. Mosby Elsevier, 2007.
Pagination
Test your knowledge.
What causes them?
Learn about your options.
What is menopause or something else
© 2005 -? 2019 WebMD LLC. OF.
WebMD does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
 Ovary Pain: 5 Causes of Pain In Ovaries, Diagnosis, Treatment
Ovary Pain: 5 Causes of Pain In Ovaries, Diagnosis, Treatment Perimenopause Ovary Pain | Ovarian Cysts | Ovulation Pain
Perimenopause Ovary Pain | Ovarian Cysts | Ovulation Pain 6 signs you've got an ovarian cyst that's about to become a big ...
6 signs you've got an ovarian cyst that's about to become a big ...:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-ovulation-pain-normal-1960292-89eed0ab32a441de9ae68973b73a2bc8.png) Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain?
Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain?/pregnancy-or-diet-concept--female-hands-protecting-the-stomach-on-white-background--840726330-59d8087e68e1a2001030b451.jpg) Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor
Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor Ovary Pain During Pregnancy: What Does It Mean?
Ovary Pain During Pregnancy: What Does It Mean? 8 Early Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer | Health.com
8 Early Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer | Health.com Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant?
Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant? Ovary pain: 7 causes
Ovary pain: 7 causes Cramping pain after your period? 8 reasons why and and when to see ...
Cramping pain after your period? 8 reasons why and and when to see ... Center for Menstrual Disorders in Rochester, NY
Center for Menstrual Disorders in Rochester, NY I have pain in my right ovary for last 10 months. Should I worry ...
I have pain in my right ovary for last 10 months. Should I worry ...:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pelvicpainfinal-01-5be8f46ec9e77c0051faa2c2.png) Pelvic Pain in Women: Causes and Treatment
Pelvic Pain in Women: Causes and Treatment Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms, & Treatment in Akron, Ohio
Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms, & Treatment in Akron, Ohio 2-week left-sided pelvic pain | MDedge ObGyn
2-week left-sided pelvic pain | MDedge ObGyn/what-are-ovarian-cysts-3520952_color3-5c454c9146e0fb0001415309.png) Ovarian Cysts: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Ovarian Cysts: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Implantation Cramping: Pregnant? Or Just Your Period?
Implantation Cramping: Pregnant? Or Just Your Period? Pain in lower right abdomen: 16 causes, diagnosis, and treatment
Pain in lower right abdomen: 16 causes, diagnosis, and treatment Pelvic & Uterine Pain: 18 Possible Causes of Pelvic Pain in Women
Pelvic & Uterine Pain: 18 Possible Causes of Pelvic Pain in Women Signs You Have an Ovarian Cyst — and What to Do About It – Health ...
Signs You Have an Ovarian Cyst — and What to Do About It – Health ... Ovary Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes, Management, and More
Ovary Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes, Management, and More Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant?
Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant? Ovarian Cyst Symptoms - How To Know If You Have An Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cyst Symptoms - How To Know If You Have An Ovarian Cyst Pain in Lower Right Abdomen Near the Hip Bone: 20 Causes
Pain in Lower Right Abdomen Near the Hip Bone: 20 Causes I mistook my ovarian cancer symptoms for IBS'
I mistook my ovarian cancer symptoms for IBS' Cramping But No Period? This Is When To See Your Doctor
Cramping But No Period? This Is When To See Your Doctor Pin on Bodies
Pin on Bodies Ovary Pain: What Is It?
Ovary Pain: What Is It? Reasons for Ovulation Pain - Ovulation Pain Causes and Treatment
Reasons for Ovulation Pain - Ovulation Pain Causes and Treatment Can You Rely on Ovarian Pain as an Early Pregnancy Sign? - 2019
Can You Rely on Ovarian Pain as an Early Pregnancy Sign? - 2019 15 Reasons for Pain on Ovary during Pregnancy
15 Reasons for Pain on Ovary during Pregnancy 5 Common Ovulation Pains — Symptoms of Ovulation
5 Common Ovulation Pains — Symptoms of Ovulation/what-happens-if-i-have-a-ruptured-ovarian-cyst-2616648-5bc3f3ac46e0fb00589b8309.png) Ruptured Ovarian Cysts: Diagnosis, Treatment, and More
Ruptured Ovarian Cysts: Diagnosis, Treatment, and More Why Does It Hurt After I Come? 8 Possible Causes Of Dysorgasmia
Why Does It Hurt After I Come? 8 Possible Causes Of Dysorgasmia Abdominal Pain and Breast Tenderness: Causes and Treatments
Abdominal Pain and Breast Tenderness: Causes and Treatments Abdominal Pain and Cramping After Sex: What You Need to Know | Allure
Abdominal Pain and Cramping After Sex: What You Need to Know | Allure 13 Medical Reasons For Abdominal Pain After Sex | Page 1 ...
13 Medical Reasons For Abdominal Pain After Sex | Page 1 ... Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens
Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens Cramping After Ovulation? What It Really Means - Conceive Success
Cramping After Ovulation? What It Really Means - Conceive Success Ovarian Cysts: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments | UNC Health Talk
Ovarian Cysts: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments | UNC Health Talk Ovary Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes, Management, and More
Ovary Pain in Early Pregnancy: Causes, Management, and More Management of Ruptured Ovarian Cyst | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Management of Ruptured Ovarian Cyst | Johns Hopkins Medicine Ovarian cysts | womenshealth.gov
Ovarian cysts | womenshealth.gov Cramps after menopause: Causes, diagnosis, and treatment
Cramps after menopause: Causes, diagnosis, and treatment Pain in Lower Right Abdomen: 16 Possible Causes
Pain in Lower Right Abdomen: 16 Possible Causes Pelvic Pain? Check These 3 Causes | Premier Health
Pelvic Pain? Check These 3 Causes | Premier Health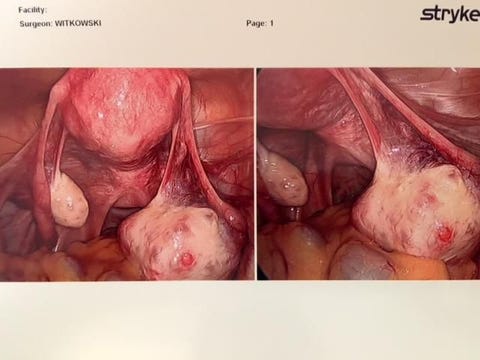 My Period Pain Was Unbearable - How to Treat a Dermoid Cyst
My Period Pain Was Unbearable - How to Treat a Dermoid Cyst Pain After Hysterectomy - Pelvic Rehabilitation Medicine
Pain After Hysterectomy - Pelvic Rehabilitation Medicine Can You Rely on Ovarian Pain as an Early Pregnancy Sign? - 2019
Can You Rely on Ovarian Pain as an Early Pregnancy Sign? - 2019 Cramps after your period: 10 causes, symptoms, and treatment
Cramps after your period: 10 causes, symptoms, and treatment Ovarian Cyst Symptoms - How To Know If You Have An Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cyst Symptoms - How To Know If You Have An Ovarian Cyst Why Do I Have Cramps but No Period? | Health.com
Why Do I Have Cramps but No Period? | Health.com Cramping pain after your period? 8 reasons why and and when to see ...
Cramping pain after your period? 8 reasons why and and when to see ... Pelvic & Uterine Pain: 18 Possible Causes of Pelvic Pain in Women
Pelvic & Uterine Pain: 18 Possible Causes of Pelvic Pain in Women
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar