 Mid cycle pain
Mid cycle pain
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina (vaginal canal) forming the female reproductive system.
Mittelschmerz is one-sided, lower abdominal pain associated with ovulation. German for "middle pain," mittelschmerz occur mid menstrual cycle - about 14 days before the next menstruation period
In most cases, mittelschmerz not require medical attention .. For mittelschmerz minor discomfort, over-the-counter painkillers sick and home remedies are often ineffective. If you are troubled mittelschmerz pain, the doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives to stop ovulation and prevent a mid-cycle pain.
Mittelschmerz pain usually lasts a few minutes to a few hours, but may continue for a day or two. Pain from mittelschmerz possible:
Mittelschmerz pain occurs in the ovary releases an egg (ovulation). The pain may switch sides every month, or you may feel pain on the same side for several months.
Keep track of your menstrual cycle for several months and records when you feel lower abdominal pain. If it happens mid-cycle and disappear without treatment, most likely mittelschmerz.
Mittelschmerz rarely require medical intervention. However, contact your doctor if new pelvic pain becomes severe, if it is accompanied by nausea or fever, or if it continues - that could indicate you have a more serious condition than mittelschmerz, such as appendicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease or ectopic pregnancy even.
Mittelschmerz occur during ovulation, when the follicle rupture and release their eggs. Some women have mittelschmerz every month; , Other people have it only intermittently
mittelschmerz exact cause is unknown, but possible reasons for pain include:
Pain at any other point in your menstrual cycle is not mittelschmerz. It may be normal menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) if it occurs during your period, or perhaps from stomach problems or other pelvic. If you have severe pain, see your doctor.
Ovulation is the release of an egg from one of her ovaries. This often happens around the middle of the menstrual cycle, although the right time can vary.
In preparation for ovulation, the uterine lining, or endometrium, thickens. stimulates the pituitary gland in the brain one ovary to release an egg. The walls are ruptured ovarian follicle in the ovary surface. the egg is released.
Finger-like structures called fimbriae sweep the egg into the fallopian tubes neighbors. The trip egg through the fallopian tube, driven in part by a contraction in the wall of the fallopian tube. Here, in the fallopian tube, the egg can be fertilized by sperm.
If the egg is fertilized, the egg and sperm unite to form a single-celled entity called a zygote. As the zygote travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus, it begins to divide rapidly to form a group of cells called the blastocyst, which resembles a small raspberry. When the blastocyst reaches the uterus, it implants in the lining of the uterus and pregnancy begins.
If the egg is not fertilized, it is only absorbed by the body - perhaps even before it reaches the uterus. About two weeks later, the womb lining shed through the vagina. This is known as menstruation.
The Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic.
Any use of this site constitutes your agreement to the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy linked below.
A copy of these materials may be reprinted for personal, non-commercial use only. "Mayo," "Mayo Clinic," "MayoClinic.org," "Mayo Clinic Healthy Living," and the triple-shield Mayo Clinic logo are trademarks of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
This site complied with the information:
 Mid cycle pain
Mid cycle pain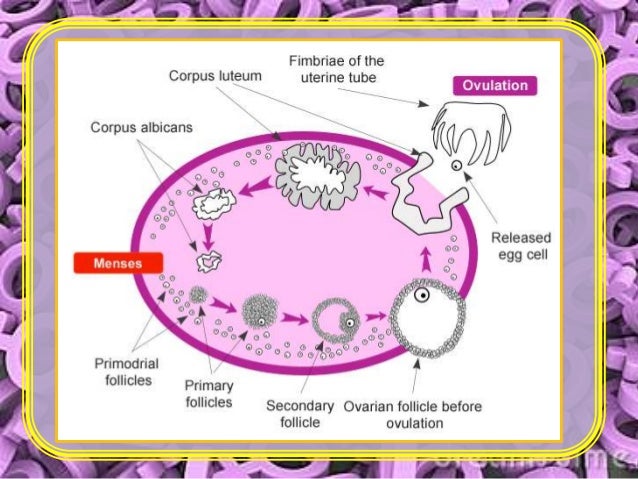 Mid cycle pain
Mid cycle pain Mid-Cycle Pain Mittelschmerz | Articles | Mount Nittany Health System
Mid-Cycle Pain Mittelschmerz | Articles | Mount Nittany Health System:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-ovulation-pain-normal-1960292-89eed0ab32a441de9ae68973b73a2bc8.png) Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain?
Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ovarypainfinal-01-5be8f3e846e0fb0051ce313d.png) Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor
Ovary Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor Mittelschmerz or Ovulation Pain or Midcycle Pain|Causes|Signs ...
Mittelschmerz or Ovulation Pain or Midcycle Pain|Causes|Signs ... Mid cycle pain
Mid cycle pain Mid cycle pain
Mid cycle pain Reasons for Ovulation Pain - Ovulation Pain Causes and Treatment
Reasons for Ovulation Pain - Ovulation Pain Causes and Treatment Endometriosis and the Menstrual Pain Cycle | MyEndometriosisTeam
Endometriosis and the Menstrual Pain Cycle | MyEndometriosisTeam Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant?
Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant? When Should You See a Doctor for Irregular Periods? – Penn Medicine
When Should You See a Doctor for Irregular Periods? – Penn Medicine Pin on Health Care
Pin on Health Care Mid-Cycle Joint Aches or Pain in Women Causes and Solutions ...
Mid-Cycle Joint Aches or Pain in Women Causes and Solutions ... Breast pain | The 3 types of breast pain and their causes
Breast pain | The 3 types of breast pain and their causes Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens
Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens/exercise-effects-on-menstruation-4104136-5c04719446e0fb0001d4639e.png) Changes Exercise May Have on Your Period
Changes Exercise May Have on Your Period:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/reasons-for-fainting-during-period-4107096-5c04ab3ec9e77c00014904c4.png) Why You May Faint During Your Period
Why You May Faint During Your Period Ovulation Bleeding and Ovulation Spotting: What it is, & Why It ...
Ovulation Bleeding and Ovulation Spotting: What it is, & Why It ...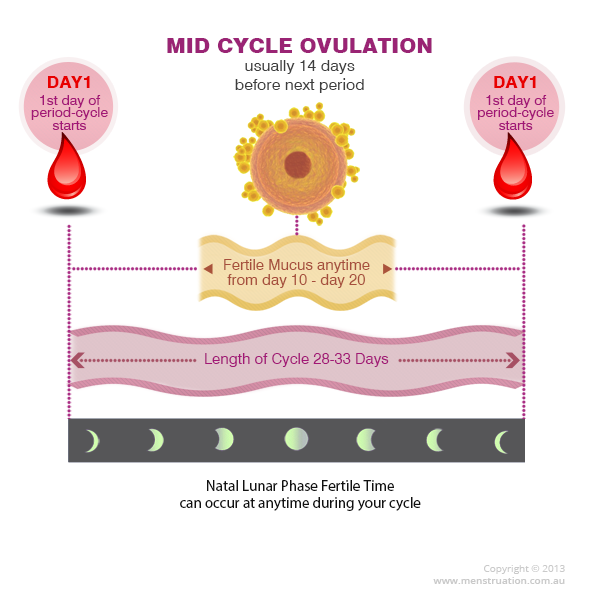 Could I be pregnant? pregnancy signs, fertile times
Could I be pregnant? pregnancy signs, fertile times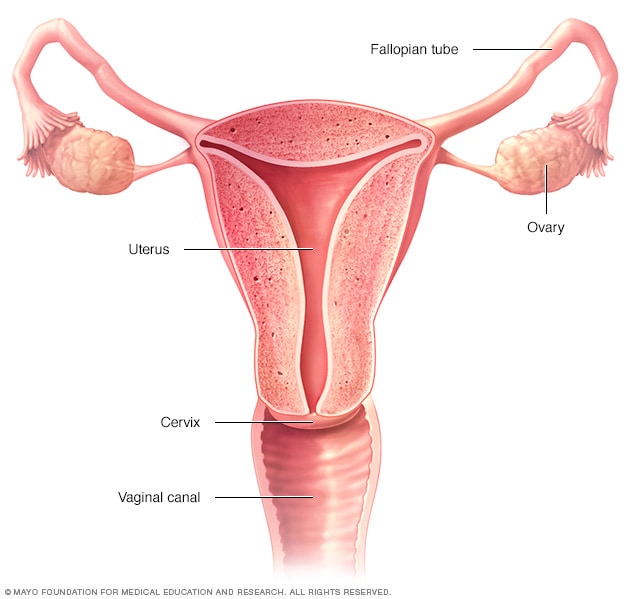 Mittelschmerz - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Mittelschmerz - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s
Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s How Long After Ovulation Pain Do You Ovulate? | LoveToKnow
How Long After Ovulation Pain Do You Ovulate? | LoveToKnow Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s
Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1960279-checking-cervical-mucus-to-get-pregnant-faster-01-5ae09ac2c06471003916b7cb.png) 8 Signs of Ovulation to Detect Your Most Fertile Time
8 Signs of Ovulation to Detect Your Most Fertile Time Ovulation Pain: Why It Shouldn't Be Ignored and When to Get Help
Ovulation Pain: Why It Shouldn't Be Ignored and When to Get Help Should I Worry? 13 Reasons for Mid-Cycle Spotting | Progesterone ...
Should I Worry? 13 Reasons for Mid-Cycle Spotting | Progesterone ... Cramping when Ovulating - Signs, Treatment | Everyday Health
Cramping when Ovulating - Signs, Treatment | Everyday Health Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant?
Cramping Pain During or After Ovulation? Are You Pregnant? Pin on Homeopathy
Pin on Homeopathy Follicular phase - Wikipedia
Follicular phase - Wikipedia:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breast-pain-cycle2-56a0b6b35f9b58eba4b30fa5.jpg) Cyclical and Noncyclical Breast Pain: Causes and Differences
Cyclical and Noncyclical Breast Pain: Causes and Differences Ultrasonography of adnexal masses: imaging findings
Ultrasonography of adnexal masses: imaging findings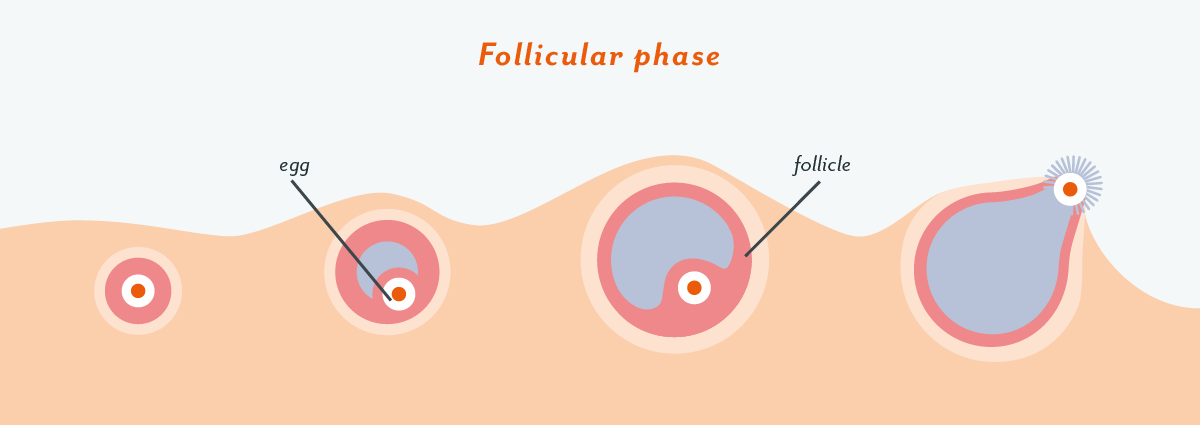 Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens
Ovulation Pain: Symptoms, How Common It is, and Why It Happens/GettyImages-84596863-58b724185f9b5880801fcab0.jpg) Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain?
Is It Normal to Experience Ovulation Pain? Evaluation of Acute Pelvic Pain in Women - American Family Physician
Evaluation of Acute Pelvic Pain in Women - American Family Physician Cramping when Ovulating - Signs, Treatment | Everyday Health
Cramping when Ovulating - Signs, Treatment | Everyday Health Abdominal and Pelvic Pain - ppt download
Abdominal and Pelvic Pain - ppt download Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s
Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s Severe Bloating During Ovulation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Severe Bloating During Ovulation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s
Why Is My Period Changing? An Infographic Before & After Your 30s Ovulation pain: Symptoms and when to see a doctor
Ovulation pain: Symptoms and when to see a doctor Why women should take abdominal pain seriously - The Economic Times
Why women should take abdominal pain seriously - The Economic Times Spotting Between Periods – Your Period
Spotting Between Periods – Your Period How to help with mid-cycle pain (mittelschmerz pain) - YouTube
How to help with mid-cycle pain (mittelschmerz pain) - YouTube Evaluation of Acute Pelvic Pain in Women - American Family Physician
Evaluation of Acute Pelvic Pain in Women - American Family Physician Lower abdominal pain in women - causes and treatments
Lower abdominal pain in women - causes and treatments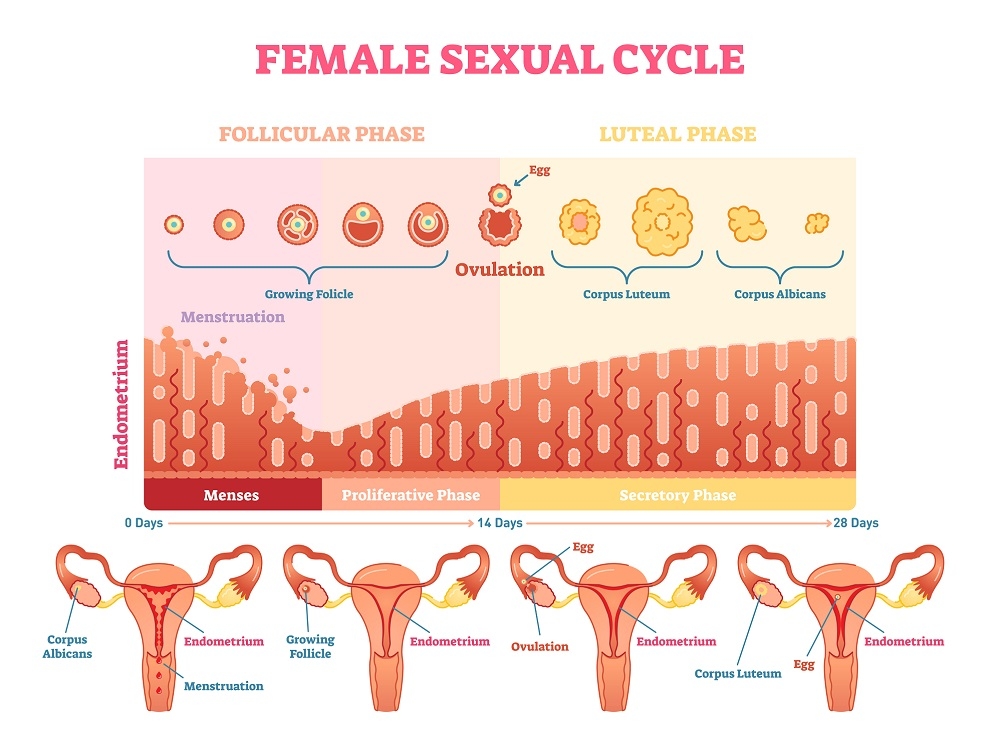 What Is Ovulation? Symptoms, Tracking, and Disorders
What Is Ovulation? Symptoms, Tracking, and Disorders:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/causes-for-sharp-breast-pain-429843-02-5b56331846e0fb0037d20241.png) Breast Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor
Breast Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor Mid cycle pain with clomid / Lower Abdomenal Pains After Clomid??
Mid cycle pain with clomid / Lower Abdomenal Pains After Clomid?? Ovulation Cramps: Signs, Causes, Tips for Conception, and More
Ovulation Cramps: Signs, Causes, Tips for Conception, and More Épinglé sur Fibroid Liver
Épinglé sur Fibroid Liver Ovulation Pain - Is It Normal To Have Ovulation Cramps
Ovulation Pain - Is It Normal To Have Ovulation Cramps Brown Discharge: What Does It Mean?
Brown Discharge: What Does It Mean?
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar