 New Study Finds That In Pregnancy One Glass Of Wine A Week Is ...
New Study Finds That In Pregnancy One Glass Of Wine A Week Is ...Thank you for contacting us. We have received your submission.
By
11 September, 2017 | 10:47
Pregnant women who drink up to two standard glasses of wine a week are unlikely to harm their unborn babies, a new study shows.
The evidence that light drinking in pregnancy or occasionally dangerous "surprisingly limited" but scientists are suggesting pregnant women are advised to avoid alcohol "just in case."
This is because there is a small risk of having underweight or premature infants if women drink up to four units a week.
previous research has shown heavy drinking during pregnancy causes birth defects, affect the intelligence of babies and causing motor problems behavioral, mental and well.
As a result, women are told to avoid strenuous or "binge drinking" but advice on the level of drinking "safe" remains a gray area.
until the current UK guidelines advise women to avoid drinking alcohol when trying to conceive, and in the first trimester.
At the same time show that consumption should be limited to withi n "1:59 UK units once or twice a week."
However, the new guidelines of the Head of the UK Department of Health recommended women should not drink alcohol at all while trying to conceive or during pregnancy, on the grounds that it was "better to be safe than sorry."
But this has left many women confused about whether there is the safe limit and if only one glass is dangerous.
problem remains of great public health importance because up to 80 per cent of mothers-to-be in the UK, Ireland, New Zealand and Australia drank alcohol during their pregnancy.
So scientists at Bristol University set out to determine the effects of low to moderate levels of drinking by women in pregnancy and long-term health effects on their children.
Research conducted a systematic review of 5,000 studies and selected 26 that looked at the effects of drinking the light of the two units up to twice a week, or four units a week, equivalent to a total of about 32 g compared with no alcohol at ll.
It looks mainly at the complications of pregnancy and birth characteristics, such as miscarriage, premature birth, and infant-sized and long-term issues, such as developmental delay, impaired intelligence and behavioral difficulties typical fetal alcohol syndrome -. the consequences of heavy drinking in pregnancy
It was found drinking up to four units a week while pregnant, on average, was associated with an eight percent higher risk of having a small baby, compared with not drinking at all.
Likewise, drink up to four units or 32g a week was associated with a 10 percent increased risk of premature birth.
Research noted in comparison, light to moderate smoke less than 20 cigarettes per day was associated with a 22 percent increased risk.
But the evidence on how much, if any, is safe to drink, or what stage of pregnancy, it is important by its absence.
The Senior Research Associate Dr Loubaba Mamluk said: "In conclusion, we fo und limited evidence for the causal role of light drinking in pregnancy, compared with abstention, the majority of results are reviewed.
"Despite the differences between drinking light and never become a point of tension and confusion for health professionals and pregnant women and contribute to the guidance consistent and advice now and in the past, a review showed our extensive that specific question is not being scrutinized closely enough, if at all.
"In addition, there has been no evidence about the possible benefits of alcohol consumption lighter than abstinence.
"Formulating guidelines while challenging the evidence base.
"However, describing the lack of current research and explains that" absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, 'appears justified.
"Women who have had a drink during pregnancy should be reassured that they might not have led to a considerable loss of their baby, but if you're worried, they sho uld discuss this with their doctor or midwife.
"Evidence of the effects of drinking up to 32 g / week in pregnancy is rare.
"Because there is some evidence that even light alcohol consumption prenatal associated with being underweight and premature births, guidance can suggest abstention as the precautionary principle."
175 ml standard glass of red, white or rose wine with ABV of 12 percent contains 2.1 units.
The study is published in the journal BMJ Open.
Share Selection
This story has been shared 239 907 times. 239 907
This story has been shared 133 407 times. 133 407
This story has been shared 110 528 times. 110 528
Subscription ,, and.
© 2020 NYP Holdings, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 A Few Drinks While Pregnant May Be OK : Shots - Health News : NPR
A Few Drinks While Pregnant May Be OK : Shots - Health News : NPR/pregnant-woman-with-glass-of-red-wine-167457193-59727baf519de200115324a0.jpg) Drinking Alcohol During Early Pregnancy
Drinking Alcohol During Early Pregnancy Drinking Red Wine During Pregnancy: Risks & Research
Drinking Red Wine During Pregnancy: Risks & Research Drinking During Pregnancy: Could Consuming Wine While Pregnant ...
Drinking During Pregnancy: Could Consuming Wine While Pregnant ... Drinking Wine during Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks & Myths
Drinking Wine during Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks & Myths Pin by What Not To Eat When Pregnant on Drinking While Pregnant ...
Pin by What Not To Eat When Pregnant on Drinking While Pregnant ... Against doctors' orders, American women are opening up about ...
Against doctors' orders, American women are opening up about ... Can Women Drink Wine While Pregnant? Science Says Maybe | Fatherly
Can Women Drink Wine While Pregnant? Science Says Maybe | Fatherly For pregnant women, one glass of wine a day is fine: study - New ...
For pregnant women, one glass of wine a day is fine: study - New ... New study shows no harm from moderate drinking in pregnancy, but ...
New study shows no harm from moderate drinking in pregnancy, but ...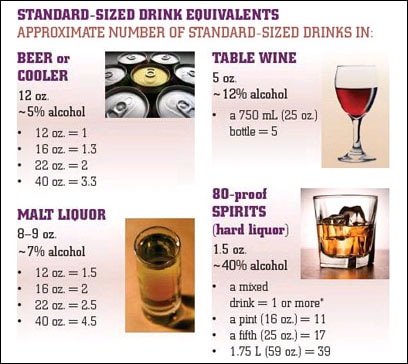 FASDs: Information for Women | CDC
FASDs: Information for Women | CDC Is One Drink OK For Pregnant Women? Around The Globe, The Answer ...
Is One Drink OK For Pregnant Women? Around The Globe, The Answer ... Am I Bad for Drinking Wine While Pregnant? - SleepBaby.org
Am I Bad for Drinking Wine While Pregnant? - SleepBaby.org I Embraced Light Drinking While Pregnant And I Have Zero Regrets
I Embraced Light Drinking While Pregnant And I Have Zero Regrets Drinking While Pregnant: How Dangerous Is It? | Taste of Home
Drinking While Pregnant: How Dangerous Is It? | Taste of Home Drinking while pregnant: No amount of alcohol is safe according to ...
Drinking while pregnant: No amount of alcohol is safe according to ... Light drinking during pregnancy does not harm baby: study
Light drinking during pregnancy does not harm baby: study A glass of wine a day while pregnant 'will not harm your baby ...
A glass of wine a day while pregnant 'will not harm your baby ... Alcohol and pregnancy facts, when to get pregnant to have a summer ...
Alcohol and pregnancy facts, when to get pregnant to have a summer ... About That Study on Pregnancy and Red Wine | Wine Folly
About That Study on Pregnancy and Red Wine | Wine Folly Drinking Wine during Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks & Myths
Drinking Wine during Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks & Myths can I Drink wine when pregnant|Maternity Coats and Jackets by ...
can I Drink wine when pregnant|Maternity Coats and Jackets by ...:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/drinking-when-trying-to-conceive-4118991-v12-163c55fbb3054736ad03e53b32925727.png) Do You Need to Stop Drinking When Trying to Conceive?
Do You Need to Stop Drinking When Trying to Conceive? Yikes! The Risk of Drinking Red Wine During Pregnancy
Yikes! The Risk of Drinking Red Wine During Pregnancy  Risks of Drinking Alcohol While Pregnant - YouTube
Risks of Drinking Alcohol While Pregnant - YouTube Pin on baby
Pin on baby The Changing Perceptions on Drinking While Pregnant | Wine ...
The Changing Perceptions on Drinking While Pregnant | Wine ... Women aren't following advice to stop drinking when pregnant
Women aren't following advice to stop drinking when pregnant Yes to Coffee and Wine: Rewriting the Rules of Pregnancy - WSJ
Yes to Coffee and Wine: Rewriting the Rules of Pregnancy - WSJ 14 women confess to drinking alcohol during pregnancy | Tommy's
14 women confess to drinking alcohol during pregnancy | Tommy's The debate: Did you drink at all during pregnancy?
The debate: Did you drink at all during pregnancy? Light drinking during pregnancy does not harm unborn baby, study ...
Light drinking during pregnancy does not harm unborn baby, study ... A Few Drinks While Pregnant May Be OK : Shots - Health News : NPR
A Few Drinks While Pregnant May Be OK : Shots - Health News : NPR Frosty, Heidi and Frank: H&F News Feed
Frosty, Heidi and Frank: H&F News Feed Pregnant women should avoid red wine because it harms unborn ...
Pregnant women should avoid red wine because it harms unborn ... Can You Drink While Pregnant? Even Light Drinking Can Cause Problems
Can You Drink While Pregnant? Even Light Drinking Can Cause Problems can I Drink wine when pregnant|Maternity Coats and Jackets by ...
can I Drink wine when pregnant|Maternity Coats and Jackets by ... Drinking a little alcohol early in pregnancy may be okay - Harvard ...
Drinking a little alcohol early in pregnancy may be okay - Harvard ... Yes, I Had Wine While Pregnant – How Do I Mom?
Yes, I Had Wine While Pregnant – How Do I Mom? Can Pregnant Women Have A Glass Of Wine With Dinner? Everything We ...
Can Pregnant Women Have A Glass Of Wine With Dinner? Everything We ... One in 10 pregnant women in the United States reports drinking ...
One in 10 pregnant women in the United States reports drinking ... Why I Drank While I Was Pregnant - Alcohol and Pregnancy - Cosmo
Why I Drank While I Was Pregnant - Alcohol and Pregnancy - Cosmo Drinking red wine while pregnant | General center | SteadyHealth.com
Drinking red wine while pregnant | General center | SteadyHealth.com Red wine during pregnancy: Is it safe?
Red wine during pregnancy: Is it safe? How Bad Is Drinking While Pregnant? Doctors Discuss Safety | Shape
How Bad Is Drinking While Pregnant? Doctors Discuss Safety | Shape Can Pregnant Women Drink Wine? | Taste of Home
Can Pregnant Women Drink Wine? | Taste of Home Are coffee, wine and sushi OK in pregnancy? New book says yes
Are coffee, wine and sushi OK in pregnancy? New book says yes Report: 1 in 9 U.S. women drink alcohol while pregnant | wzzm13.com
Report: 1 in 9 U.S. women drink alcohol while pregnant | wzzm13.com 14 women confess to drinking alcohol during pregnancy | Tommy's
14 women confess to drinking alcohol during pregnancy | Tommy's Red Wine During Pregnancy: Does New Research Suggest It's Safe?
Red Wine During Pregnancy: Does New Research Suggest It's Safe? Local Bars and Restaurants Urge Pregnant Women Not to Drink
Local Bars and Restaurants Urge Pregnant Women Not to Drink
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar