 Vaginal Burning Symptoms, Relief & Treatment
Vaginal Burning Symptoms, Relief & Treatment© 1996-2018 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved.
MedicineNet does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. ,
/ // / vaginal pain (vulvodynia) Articles
Vulvodynia refers to pain in the vulva and vagina. Vulvodynia is considered ill that no known cause. This is different from the pain that lies deep in the pelvis or vagina internally. This article focuses on the pain in the vulva and the opening (introitus) of the vagina. pain in the vagina deeper can also occur due to infection, tumor, and the more common condition that causes pain in the pelvic organs.
Pain in the vagina or the female external genitalia (vulva, including the labia, clitoris, and the entrance to the vagina) is the most common result of an infection. Vaginitis is another term for vaginal infections. yeast infections (Candida) is a very common form of vaginitis. Women are at increased risk for yeast vaginitis if they take antibiotics or cortisone medications, during pregnancy, and if their immune systems are suppressed by medications or illness. vaginal pain can also be the result of injury or trauma to the vagina or vulva. pain in the vagina during sexual intercourse is called dyspareunia. The medical term for vaginal pain vulvodynia.
The pain of vulvodynia can be debilitating and interfere with daily activities and sexual intercourse. It can make a woman feel to lose control of their bodies, causing physical and emotional discomfort depth
The symptoms of vulvodynia and pain in the vagina may include :.
Some women report pain localized to one side or the vulva area, while others have more general and widespread pain. Usually, there are no physical signs or changes occur in and around the vagina with vulvodynia; However, sometimes the skin can become inflamed.
vaginal pain may occur during off due to increased pressure on the cervix. Women who have vulvodynia before it can continue to experience these symptoms during pregnancy.
It is not clear why some women experience vulvodynia. It is not considered to be related to sexually transmitted diseases (), although some women with vulvodynia have had some STDs. Some theories suggest that vulvodynia may be associated with the
Familial or genetic factors have also been proposed to play a role in vulvodynia. Unfortunately, the exact cause has not been determined, and most women have no known factors.
Since the cause is poorly understood, it is difficult to predict who is at risk for vulvodynia. It can affect women of all ages and races. It can start as early as a teenager and can occur both before and after. This may occur during or independent of the menstrual period.
There is no specific test to confirm vulvodynia. Typically, vaginal pain and vulvodynia is diagnosed based on symptoms characteristic of the condition. However, because of vulvar and vaginal infections, (eg, yeast infections, and) are associated with the burning of the vagina and, cultural or other diagnostic tests may be ordered to get rid of vaginal infections.
Vulvodynia is a chronic condition (may last for months to years) in some women; in others, it can come and go. Vulvodynia and vaginal pain can be managed with the use of medical care and self-care (home remedies). Not all treatments will work for every woman, and a woman may have to try different treatments to find the most effective option for him.
Vulvodynia is not associated with or with serious medical illness, but it may be the source and emotional discomfort for some women
some drugs that have been useful include :.
Another medical therapy for women with vulvodynia worse include:
by clicking Submit, I agree with MedicineNet these Terms & and understand that I can get out of the subscription MedicineNet any time
.
Home Remedies and self-care measures for vulvodynia can bring relief for many women. Some self-care measures to ease the pain of vulvodynia include:
vaginal yeast infections in women are caused by an organism called Candida albicans. Symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection include vaginal pain with urination, vaginal discharge, odor, and itching.
Treatment generally OTC. A man can contract a yeast infection of the female sex partners. Symptoms of yeast infection include itching of the penis in men. Treatment with oral or topical medication.
© 1996-2020 MedicineNet, Inc. All rights reserved.
MedicineNet does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. ,
 Aidance Official Site – Home of Terrasil® Skincare & Dermatology ...
Aidance Official Site – Home of Terrasil® Skincare & Dermatology ... Terrasil Rapid-Relief Vaginal Ointment Plus Medicated Cleansing ...
Terrasil Rapid-Relief Vaginal Ointment Plus Medicated Cleansing ... Vagisil Maximum Strength Anti-Itch Creme, 1 Oz, 1 Pack - Walmart ...
Vagisil Maximum Strength Anti-Itch Creme, 1 Oz, 1 Pack - Walmart ... AZO Urinary Pain Relief® | #1 Most Trusted Brand for UTI Pain
AZO Urinary Pain Relief® | #1 Most Trusted Brand for UTI Pain Top 10 Vaginal Pain Causes and Treatment Relief Options | Buoy
Top 10 Vaginal Pain Causes and Treatment Relief Options | Buoy AZO Yeast® Plus Helps to Relieve Symptoms of Vaginal Infection*
AZO Yeast® Plus Helps to Relieve Symptoms of Vaginal Infection* Amazon.com: Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer Gel ...
Amazon.com: Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer Gel ... Vaginal pain: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Vaginal pain: Causes, symptoms, and treatment Monistat 1 Day or Night Combination Pack Vaginal Antifungal ...
Monistat 1 Day or Night Combination Pack Vaginal Antifungal ... Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer GEL for Vaginal ...
Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer GEL for Vaginal ... Amazon.com: AZO Urinary Pain Relief Maximum Strength | Fast relief ...
Amazon.com: AZO Urinary Pain Relief Maximum Strength | Fast relief ... Syren Intimate Relief – Moisturizing Pain Relief Gel for Vulva and ...
Syren Intimate Relief – Moisturizing Pain Relief Gel for Vulva and ... Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief
Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief Amazon.com : Gentlepack Reusable Perineal Ice & Heat Packs with ...
Amazon.com : Gentlepack Reusable Perineal Ice & Heat Packs with ... VAGINAL ATROPHY: Vaginal Dryness, Itching, Pain or Irritation ...
VAGINAL ATROPHY: Vaginal Dryness, Itching, Pain or Irritation ... Vaginal Pain During Pregnancy: Causes, Remedies & Treatment
Vaginal Pain During Pregnancy: Causes, Remedies & Treatment URISTAT® Pain Relief Tablets
URISTAT® Pain Relief Tablets Sore Vagina After Sex: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments for Pain
Sore Vagina After Sex: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments for Pain Methods of pain relief among the women who had a vaginal delivery ...
Methods of pain relief among the women who had a vaginal delivery ... Anal Grease Sex Lubricant Anal Analgesic Base Hot Lube And Pain ...
Anal Grease Sex Lubricant Anal Analgesic Base Hot Lube And Pain ... What You Need to Know About Vaginal Pain
What You Need to Know About Vaginal Pain Sex Personal Lubricant Water Based Lube Pain Relief Anti pain Anal ...
Sex Personal Lubricant Water Based Lube Pain Relief Anti pain Anal ... Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief
Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief Vaginal Pain during Pregnancy: Types, Causes and Treatment
Vaginal Pain during Pregnancy: Types, Causes and Treatment Pregnancy Vaginal Pain - Causes & Tips for Relief | Pregnant Pain
Pregnancy Vaginal Pain - Causes & Tips for Relief | Pregnant Pain Vagisil Maximum Strength Medicated Anti-Itch Creme - 1 oz.
Vagisil Maximum Strength Medicated Anti-Itch Creme - 1 oz. Vaginal Pain During Pregnancy|Causes|Ways to Relieve it
Vaginal Pain During Pregnancy|Causes|Ways to Relieve it Balneol Hygienic Cleansing Lotion for Anal or Vaginal Discomfort ...
Balneol Hygienic Cleansing Lotion for Anal or Vaginal Discomfort ... Vaginal cuts and tears: Causes, treatment, and when to see a doctor
Vaginal cuts and tears: Causes, treatment, and when to see a doctor:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pelvicpainfinal-01-5be8f46ec9e77c0051faa2c2.png) Pelvic Pain in Women: Causes and Treatment
Pelvic Pain in Women: Causes and Treatment Menstrual Period Instant Pain Relief Solution Cramps No Side ...
Menstrual Period Instant Pain Relief Solution Cramps No Side ... Queen V The Eraser Yeast Infection Treatment, 14 Vaginal ...
Queen V The Eraser Yeast Infection Treatment, 14 Vaginal ... FORIA Relief Vaginal Cannabis Tampons | for Women
FORIA Relief Vaginal Cannabis Tampons | for Women/vaginal-itching-3521009-5c3b8d2646e0fb000101c775.png) Vaginal Itching During Pregnancy Causes and Treatment
Vaginal Itching During Pregnancy Causes and Treatment Sex Shop Water Soluble Vaginal Lubricants Anal Pain Relief ...
Sex Shop Water Soluble Vaginal Lubricants Anal Pain Relief ... Pelvic physical therapy: Another potential treatment option ...
Pelvic physical therapy: Another potential treatment option ... Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief
Pin on SYREN Intimate Relief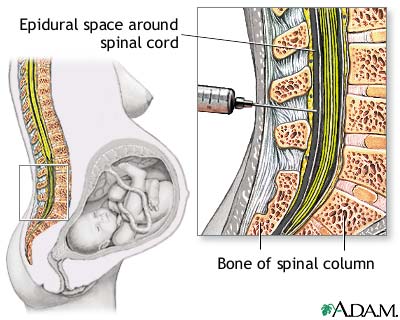 Vaginal birth - series—Procedure, part 1: MedlinePlus Medical ...
Vaginal birth - series—Procedure, part 1: MedlinePlus Medical ... Walgreens Clotrimazole Vaginal Cream | Walgreens
Walgreens Clotrimazole Vaginal Cream | Walgreens![Amazon.com: [Kangyacare] Qian Jin Pian - Flemingia Herbal Pills ... Amazon.com: [Kangyacare] Qian Jin Pian - Flemingia Herbal Pills ...](https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/I/41jw5vdcHVL._AC_SY400_.jpg) Amazon.com: [Kangyacare] Qian Jin Pian - Flemingia Herbal Pills ...
Amazon.com: [Kangyacare] Qian Jin Pian - Flemingia Herbal Pills ... Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer Gel for Vaginal ...
Syren Intimate Relief | Best Soothing Moisturizer Gel for Vaginal ... IMVEXXY (estradiol vaginal inserts) Treatment for Painful Sex Due ...
IMVEXXY (estradiol vaginal inserts) Treatment for Painful Sex Due ... vaginal birth | Pregnancy in Dubai
vaginal birth | Pregnancy in Dubai Almost) Everything You've Wanted to Know About Vaginal Dryness ...
Almost) Everything You've Wanted to Know About Vaginal Dryness ... AZO Yeast® Plus Helps to Relieve Symptoms of Vaginal Infection*
AZO Yeast® Plus Helps to Relieve Symptoms of Vaginal Infection* Women's Wellness: Painful sex after menopause – Mayo Clinic News ...
Women's Wellness: Painful sex after menopause – Mayo Clinic News ... Vaginal Pressure During Pregnancy: Is It Normal?
Vaginal Pressure During Pregnancy: Is It Normal? Vaginal Sterile Lubricant Gel Vaginal Pain Relief Vagina Intimate ...
Vaginal Sterile Lubricant Gel Vaginal Pain Relief Vagina Intimate ...:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vaginal-yeast-infections-overview-3521202_color1-5c773bccc9e77c0001e98dc1.png) Yeast Infection: Overview and More
Yeast Infection: Overview and More AZO Urinary Tract Health Support Pack | 18 Urinary Pain Relief ...
AZO Urinary Tract Health Support Pack | 18 Urinary Pain Relief ... Vaginal Pain from pelvic and spinal ligament injury – Caring Medical
Vaginal Pain from pelvic and spinal ligament injury – Caring Medical Vaginal Soreness → Learn How to Avoid and Treat a Sore Vagina
Vaginal Soreness → Learn How to Avoid and Treat a Sore Vagina VH Essentials Vaginal Odor Treatment (with Photos, Prices ...
VH Essentials Vaginal Odor Treatment (with Photos, Prices ... Personal Smooth Lubricant Water Soluble Pain Relief Gel Lubricants ...
Personal Smooth Lubricant Water Soluble Pain Relief Gel Lubricants ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar