 MY MISCARRIAGE STORY AT 6 WEEKS PREGNANT!!! - YouTube
MY MISCARRIAGE STORY AT 6 WEEKS PREGNANT!!! - YouTubeAn estimated 15 to 20 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage, loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week. The actual number may be higher because many miscarriages occur very early, before a woman knows she is pregnant, and just might seem to be a heavy period on or near schedule.
Most of the clinically recognized miscarriages occur between seven and 12 weeks after a woman's last menstrual period. Possible miscarriage decline significantly once a heartbeat has been detected on ultrasound or by Doppler stethoscope
Most of miscarriage (also called spontaneous abortion) can not be prevented .; they are random events that are not likely to be repeated. Up to 70 percent of miscarriage in the first trimester, and 20 percent of second-trimester miscarriage, caused by a chromosomal anomaly.
Other known causes include infection, uterine or cervical abnormalities, smoking, substance abuse, exposure to environmental toxins or industrial, diabetes, thyroid disease, and autoimmune diseases.
older women are more likely to have a miscarriage than younger women. serious physical trauma can also cause miscarriage. In rare cases, a woman suffered a miscarriage after diagnostic tests, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis. Most of the time, the specific causes of miscarriage are not identified.
Many women learn about miscarriage on a routine prenatal visit before experiencing physical symptoms. Sometimes there is no visible embryo on ultrasound, or embryo may be much smaller than expected, or without a flash. The first symptoms of miscarriage usually spotting or bleeding, followed by cramps in the lower back or abdomen. Other signs include fluid or tissue passing from the vagina.
About 1 in 4 women experience some vaginal bleeding or spotting during their first trimester. If the bleeding is mild and lasts only one to two days, with a greater risk of miscarriage. However, heavy bleeding associated with miscarriage; approximately 1 in 4 women who experience heavy bleeding would go to miscarriage. If you have vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, the doctor can help determine whether the bleeding tends to result in a miscarriage.
If your miscarriage, bleeding will become heavier and cramps can be painful as cervical dilatation. Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy can cause bleeding and pain, so if you have pain or severe risk factors for ectopic such as ectopic previous IUD use current, previous pelvic infection or infertility, seek medical treatment immediately. Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency because of the risk of internal bleeding.
If a blood test or sonogram shows that you have a miscarriage, you may have several options. Some women choose to allow miscarriages occur and resolve itself naturally. Others find that the scheduling procedure to empty the uterus gives a sense of control and closure; it also reduces the risk of infection and excessive bleeding.
There are several different treatments to complete the miscarriage. In early pregnancy you can take medications, such as misoprostol, which causes uterine contractions and miscarriage. Or minor surgical procedures (suction curettage, also known as dilation and curettage, or D & C) using the aspiration technique to remove the remaining tissue. Both of these are outpatient procedures. Aspiration can be performed on an outpatient basis in clinics, obstetrics office, hospital, or emergency room, with or without anesthesia.
If you do not know your blood type, you should have a blood test. If your blood type is Rh-negative, you will need a shot within 72 hours of miscarriage. (If you are Rh-negative and you are carrying a fetus is Rh-positive, there is a small chance that you have been exposed to blood cells Rh-positive fetal tissue during a miscarriage. A shot of RhoGAM prevent your body produce antibodies Rh-positive blood that could harm a fetus during future pregnancies.)
If you have a miscarriage naturally or with medication, you may be complete miscarriage at home. This process may be faster or it may take several days. If you are less than eight weeks pregnant when the abortion occurs, the network will look different expelled from heavy menstrual bleeding. The further along you are in pregnancy, heavier bleeding and severe cramping. You may view the fetus and placenta.
Try to arrange reliable, knowledgeable person to be with you through the process, all night if necessary. Think about where you will be most comfortable and what you will need, such as bed liners and pads or hot water bottles and massage to comfort you and help with cramps. Your service provider may offer pain medication to help you get through.
You might want to think and talk about what you want to do with the remains. There will be some blood clots, and you may see a more powerful network or lumpy looks, which is the placenta or umbilical cord tissue. You may or may not see the network that looks like an embryo or fetus. If this is repeated (not the first) miscarriage, you may want to save the network for testing.
Once everything is in the womb you have been driven out, the bleeding will continue, reduce for a few days. If bleeding is increased or remained bright red, or if you have a debit or fever or cramps persistent, contact your health care provider to stink. If the pregnancy tissue remains in your womb, your provider can do a D & C to remove them and thus prevent infection. A D & C involves dilate the cervix and use suction (aspiration) and / or a medical instrument called a curette to remove the remainder of the pregnancy tissue.
Once the bleeding has stopped and the cervix is closed, you can have sex insertive without excess risk of infection. Because it is difficult to know when the cervix has been completely closed, most of the providers were advised to wait two weeks. A re-test after a few weeks of pregnancy is important to ensure your pregnancy hormone levels had returned to normal. If you feel dizzy or tired, tell your doctor so you can be checked for anemia.
First-trimester miscarriage is most likely a random event, it is unlikely to recur. If you have two or more early miscarriages, medical tests to help identify the cause is recommended. If you are at home when you have a miscarriage, you may be able to collect fetal tissue or placenta in a clean container for examination in a hospital-based laboratories. Put the network in a clean glass jar and refrigerate until you can take it to your service provider for testing. Ask to see the pathology report, and asked for a full explanation of all the terminology.
Blood tests in the elderly can identify or rule out hormonal disorders, immunology, or chromosomes. Examination of the womb with ultrasound, hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingography, and / or endometrial biopsy can also provide important information. Even if the cause can not be determined after the test - which often happens - you will gain knowledge. You may be able to rule out possible causes of recurrent miscarriages and at least know that you have done all you can to get an answer.
physical recovery from a miscarriage ranges from several days to several weeks. Your period will return within four to eight weeks. emotional recovery tends to take longer. Take the time to grieve, seek medical explanation if any, and find other women who had miscarried.
 Miscarriage Myths | Parents
Miscarriage Myths | Parents What can cause a miscarriage in 6 weeks of pregnancy and how can ...
What can cause a miscarriage in 6 weeks of pregnancy and how can ... First Trimester Miscarriage at 6 1/2 Weeks Gestation - What it ...
First Trimester Miscarriage at 6 1/2 Weeks Gestation - What it ... 17 Common Causes and Dangerous Risk Factors of Miscarriage
17 Common Causes and Dangerous Risk Factors of Miscarriage 6 Really Common Things That Can Cause A Miscarriage
6 Really Common Things That Can Cause A Miscarriage Miscarriage at 6 weeks Pregnant: Signs, symptoms, Causes, Risks, Rates
Miscarriage at 6 weeks Pregnant: Signs, symptoms, Causes, Risks, Rates The miscarriage: what is it? Causes, Symptoms and Treatment ...
The miscarriage: what is it? Causes, Symptoms and Treatment ... 6 early miscarriage symptoms all pregnant women need to know ...
6 early miscarriage symptoms all pregnant women need to know ... 6 weeks pregnant – all you need to know | Tommy's
6 weeks pregnant – all you need to know | Tommy's Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms & Causes | Live Science
Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms & Causes | Live Science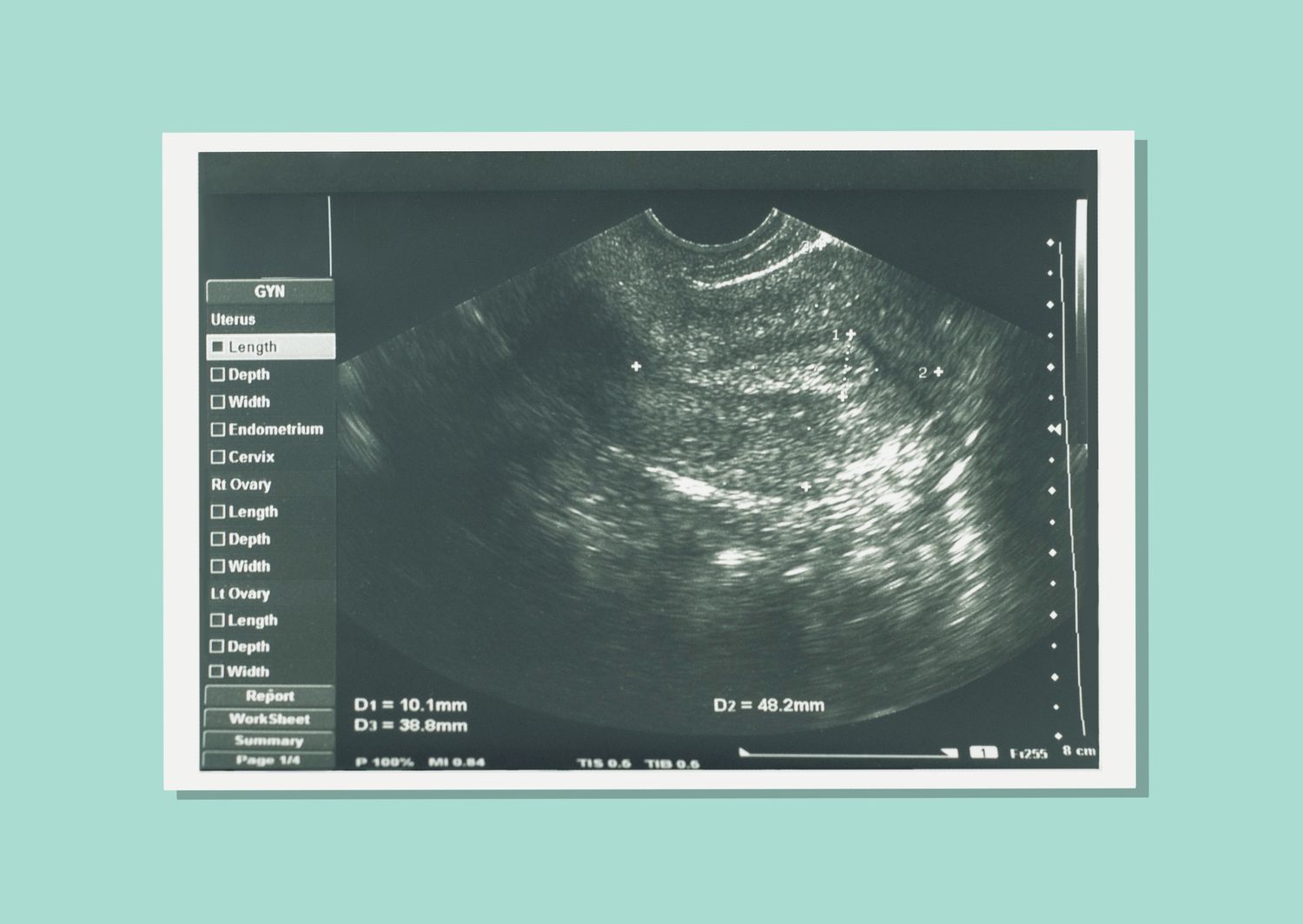 Signs of Miscarriage: When Should I Worry? | Parents
Signs of Miscarriage: When Should I Worry? | Parents How to tell you're having a miscarriage: signs and symptoms
How to tell you're having a miscarriage: signs and symptoms No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF
No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF How long does a miscarriage last?
How long does a miscarriage last? Late Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery
Late Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery What does a miscarriage feel like? 5 signs to look for
What does a miscarriage feel like? 5 signs to look for What is a missed miscarriage
What is a missed miscarriage What Causes Miscarriage to Happen? | Parents
What Causes Miscarriage to Happen? | Parents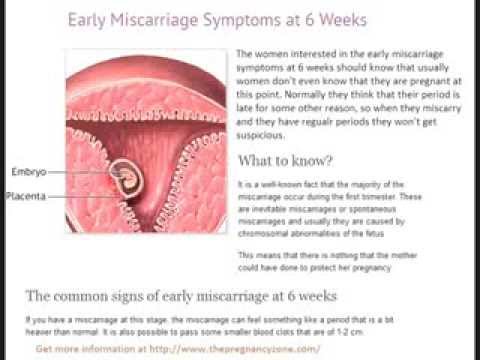 Miscarriage and Abortions in Pregnancy - YouTube
Miscarriage and Abortions in Pregnancy - YouTube Foods that can cause miscarriage | The Times of India
Foods that can cause miscarriage | The Times of India:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-81171329-597a12df22fa3a0010c17358.jpg) 10 Things You Didn't Know About Miscarriages
10 Things You Didn't Know About Miscarriages MY MISCARRIAGE STORY AT 6 WEEKS PREGNANT!!! - YouTube
MY MISCARRIAGE STORY AT 6 WEEKS PREGNANT!!! - YouTube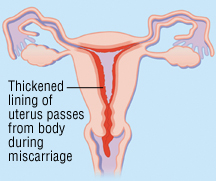 Miscarriage - Harvard Health
Miscarriage - Harvard Health Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis
Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis 5-6 WEEKS PREGNANT ????????| MISCARRIAGE SCARE | BELLY SHOT, SYMPTOMS ...
5-6 WEEKS PREGNANT ????????| MISCARRIAGE SCARE | BELLY SHOT, SYMPTOMS ... Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks
Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks Miscarriage - Wikipedia
Miscarriage - Wikipedia Causes of miscarriage | Tommy's
Causes of miscarriage | Tommy's Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics
Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics Miscarriage Without Bleeding: How to Tell
Miscarriage Without Bleeding: How to Tell What to Expect after a Miscarriage? Life after Pregnancy Loss
What to Expect after a Miscarriage? Life after Pregnancy Loss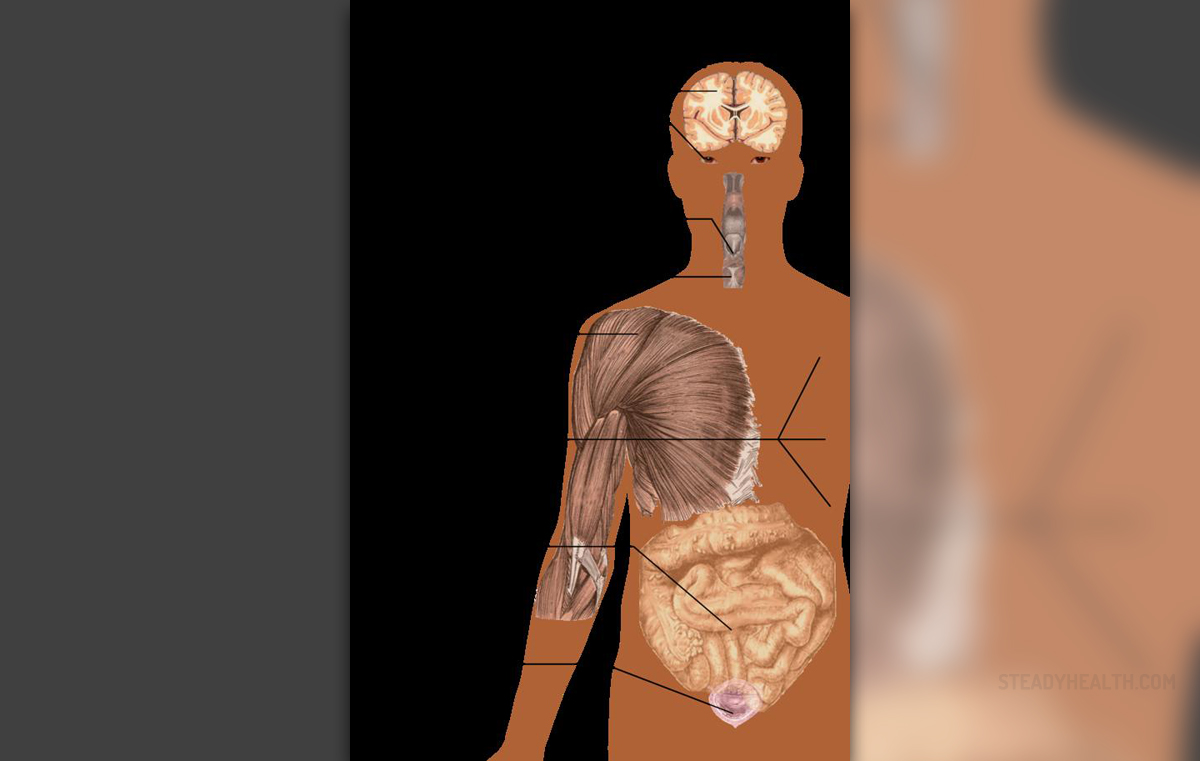 Symptoms of miscarriage at 6 weeks | General center | SteadyHealth.com
Symptoms of miscarriage at 6 weeks | General center | SteadyHealth.com No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF
No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF Early Miscarriage Symptoms at 6 Weeks Pregnancy Signs & Symptoms
Early Miscarriage Symptoms at 6 Weeks Pregnancy Signs & Symptoms Why I Wish People Talked More About Miscarriages
Why I Wish People Talked More About Miscarriages 22 Miscarriage Foods To Avoid During Pregnancy
22 Miscarriage Foods To Avoid During Pregnancy What Does a Miscarriage Look Like? Bleeding, Duration, and More
What Does a Miscarriage Look Like? Bleeding, Duration, and More what can cause a miscarriage at 6 weeks Archives - Star Styles ...
what can cause a miscarriage at 6 weeks Archives - Star Styles ... What Causes Miscarriage to Happen? | Parents
What Causes Miscarriage to Happen? | Parents 6 early miscarriage symptoms all pregnant women need to know ...
6 early miscarriage symptoms all pregnant women need to know ... Vaginal Bleeding in Early Pregnancy | One Medical
Vaginal Bleeding in Early Pregnancy | One Medical I had eight miscarriages – pregnancy can be a scary place ...
I had eight miscarriages – pregnancy can be a scary place ... Part one: What are the common causes of miscarriage? | Your ...
Part one: What are the common causes of miscarriage? | Your ... What Does It Really Mean to Be 6 Weeks Pregnant? - The New York Times
What Does It Really Mean to Be 6 Weeks Pregnant? - The New York Times Miscarriage: Signs, causes, and treatment | BabyCenter
Miscarriage: Signs, causes, and treatment | BabyCenter Miscarriage: Warning signs, treatments, and prevention
Miscarriage: Warning signs, treatments, and prevention:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/does-early-pregnancy-bleeding-mean-a-miscarriage-2371230-final-d53b152513264d6cb5ee7a65c138e097.png) Does Early Pregnancy Bleeding Mean a Miscarriage?
Does Early Pregnancy Bleeding Mean a Miscarriage? 6 weeks pregnant: Advice, symptoms, what to expect and how big is ...
6 weeks pregnant: Advice, symptoms, what to expect and how big is ...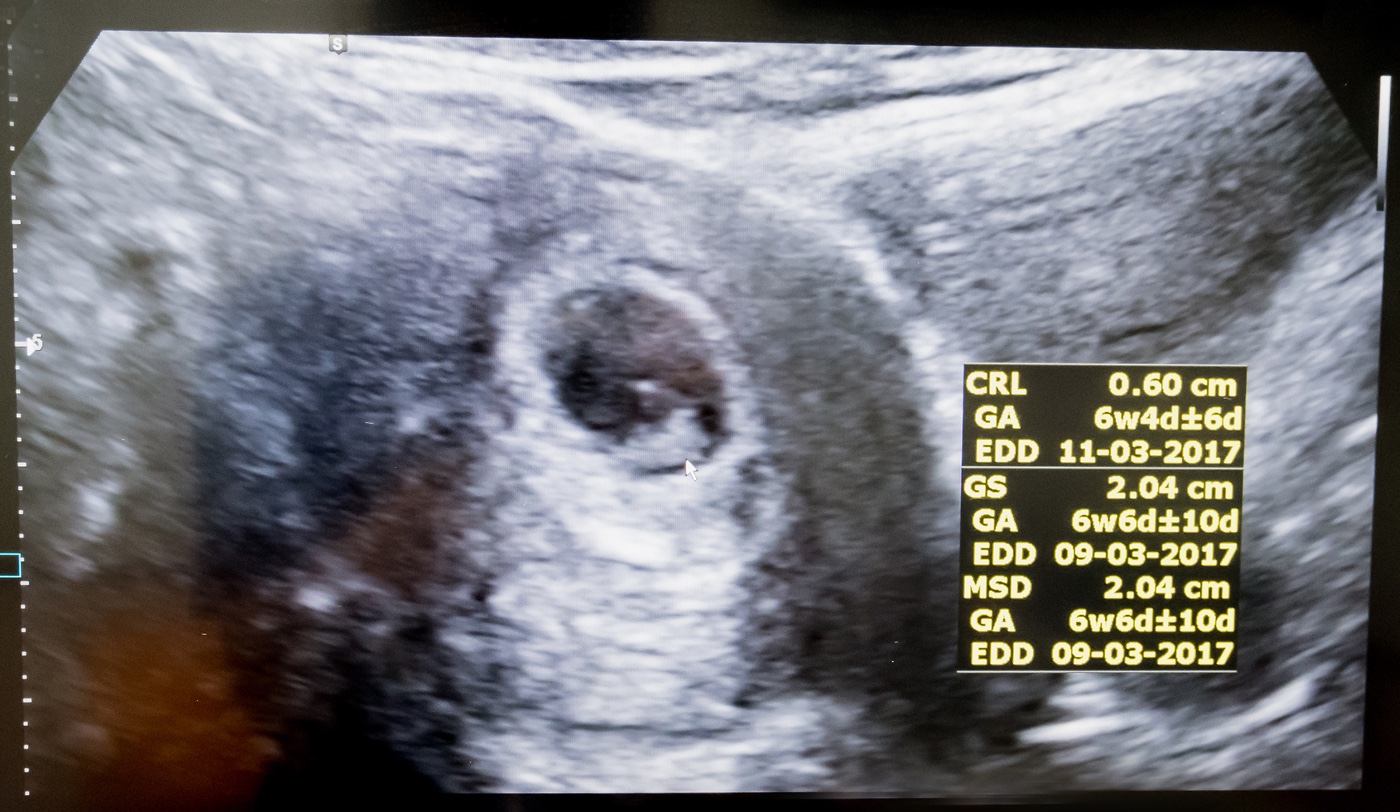 Is a 'Fetal Heartbeat' Really a Heartbeat at 6 Weeks? | Live Science
Is a 'Fetal Heartbeat' Really a Heartbeat at 6 Weeks? | Live Science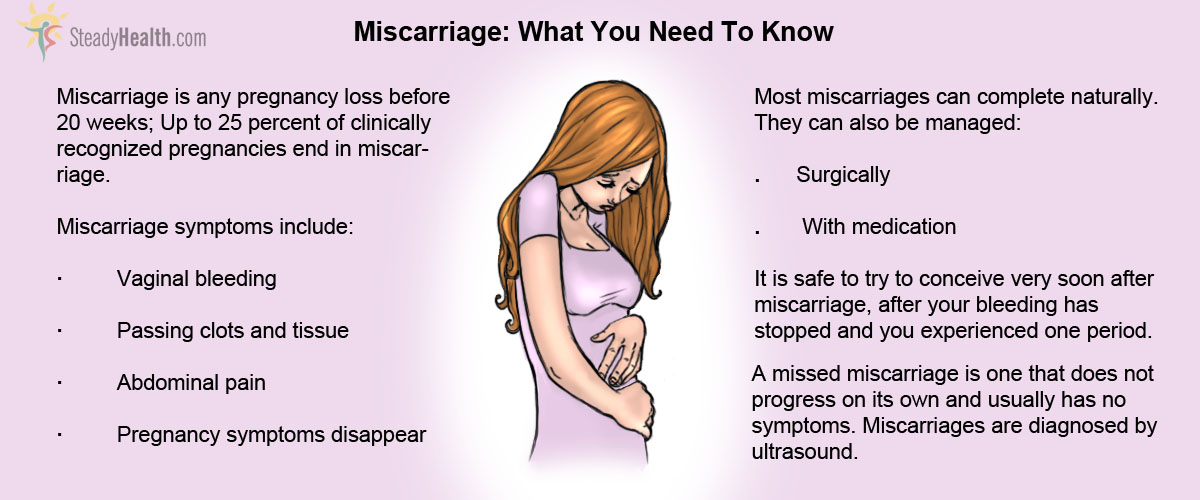 Miscarriage And Causes
Miscarriage And Causes Health Facts: Abortion with Pills and Spontaneous Miscarriage - NWHN
Health Facts: Abortion with Pills and Spontaneous Miscarriage - NWHN Eating these fruits during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage ...
Eating these fruits during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar