 Chance of miscarriage after vis. heart beat? - BabyCenter
Chance of miscarriage after vis. heart beat? - BabyCenterUltrasound scans in pregnancy may be routine or they may be offered for pain or bleeding or due to problems in previous pregnancies.
There are two ways to perform an ultrasound scan.
in early pregnancy, especially before 11 weeks, usually to have (internal) trans-vaginal scan, where the probe is placed in the vagina. This gives a clear picture and most accurate in early pregnancy. It can also be offered after 11 or 12 weeks if the trans-abdominal scan does not give a clear enough picture.
Of the 11 or 12 weeks, including in the booking-scan routine, it is more common to have a trans-abdominal scan. People who spread a special gel scan on the lower abdomen (below the navel and above the pubic hair line). He then moves the scanner over the gel, sometimes pressing, until the uterus (womb), and pregnancy can be seen.
If you do not want trans-vaginal scan, you can request a trans-abdominal scan. Which can provide some information about your pregnancy, but it is less clear than the internal scan and that might delay the diagnosis.
There is no evidence that having vaginal or abdominal scan will cause a miscarriage or harm the baby. If you bleed after vaginal scan, it will most likely be because there is a higher pooled blood in the vagina and probe dislodged it.
An ultrasound scan may be able to detect pregnancy and heart rate in normal pregnancy about 6 weeks, but this varies widely and is usually not recommended. All too often, a scan at 6 weeks showed very little or nothing, even the perfect pregnancy develops, while waiting for a week or 10 days would make the findings more clearly.
Most pregnant women referred to their first routine (or reservation) ultrasound scan somewhere between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. The purpose of the scan are:
Some women may be offered a nuchal scan between 11 and 14 weeks. The purpose of this scan is to try to detect multiple chromosomal abnormalities, such as Downs syndrome.
Many hospitals also offer further anomaly scan at 20 weeks, making a more detailed examination of the baby's development.
You can find out more about the routine, neck and anomaly scan at the website of charity
Unfortunately, sometimes the scan showed that the baby had died, perhaps a few weeks earlier and often unmarked -sign or symptoms such as bleeding or pain. This is often called a "miss", "silent" or "delayed" miscarriage. This may come as a surprise that is quite large and may take some time before you can take this information in.
You also may have to make some tough decisions about how to manage the process of miscarriage. You can read more about this
You may be referred for an initial scan because of vaginal bleeding or spotting, or perhaps because you have problems with a previous pregnancy.
The best time to have a scan is from about 7 weeks gestation when it should be possible to see the baby's heartbeat in a normal pregnancy. But it would be difficult to detect a heartbeat in early pregnancy and in those cases it would be difficult to know whether the baby had died or not developed at all, or whether it is just smaller than expected but still growing.
for that reason, you may be asked to return for another week scan or later. At that point, people who scan will be looking for a marked difference in the size of the gestational sac and the baby develop and heartbeat.
Sometimes, it can take several scans before you know sure what happened. It can be very stressful to deal with this uncertainty - some women describe as "in limbo". You may need to find some support for yourself if this happens to you.
If the scan does not take a snap and the baby seems to be the right size according to your date, it can be very convincing, even if you are still bleeding.
among women with a history of recurrent miscarriage has shown that those who see the heartbeat at 6 weeks gestation have a 78% chance of pregnancy progresses. It also suggests that seeing the heartbeat at 8 weeks increase the chances of pregnancy continues to 98% and at 10 weeks rose to 99.4%.
The figures may be even more positive for women without previous miscarriages.
So things can go wrong and sadly they sometimes do, but as long as there is a heartbeat, the risk of miscarriage decreases as the weeks go by.
In some cases, if there are no signs of pregnancy in the womb, you may be given a blood test and may be asked to return two days later for a retest.
This blood test measures the levels of pregnancy hormones ßhCG. In normal pregnancy develops hormone levels double every 48 hours and if the pattern is different, this may help to identify what happened in pregnancy.
If there are no signs of pregnancy in the womb and you have symptoms suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy, you are more likely to have blood tests and investigations called laparoscopy, which is done under general anesthesia. You can read more about this in our leaflet
ultrasound scan can show :.
In all these situations, the pregnancy will be fully miscarriage with time, but there are several ways to manage the process. You may be offered a choice, or a hospital may make recommendations. In most cases, you should be able to have time to think about what you are best able to cope. You can read more
This leaflet explains what is a blighted ovum - .. And the different medical terms that can be used when diagnosed
An ectopic pregnancy can be very distressing and frightening experience. The purpose of this leaflet to explain what is ectopic pregnancy, to provide information and answer some of the most common questions about both facts and feelings. We hope this will help what can be a very difficult time.
Miscarriage Association of Supporting the e-newsletter is sent every two months. E-newsletter containing our latest news and information about the job you have chosen to support, as well as the opportunity to engage in various campaigns and fund-raising activities. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Registered Charity No. 1076829 (England and Wales) SC039790 (Scotland). company registration No: 3779123. Registered in England and Wales.
Web Design & Development with
 Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science Miscarriage after seeing a heartbeat? - August 2016 - BabyCenter ...
Miscarriage after seeing a heartbeat? - August 2016 - BabyCenter ... Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science/GettyImages-480436845-56dfadd63df78c5ba054e56d.jpg) Miscarriage After Detecting a Heartbeat on Ultrasound
Miscarriage After Detecting a Heartbeat on Ultrasound Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science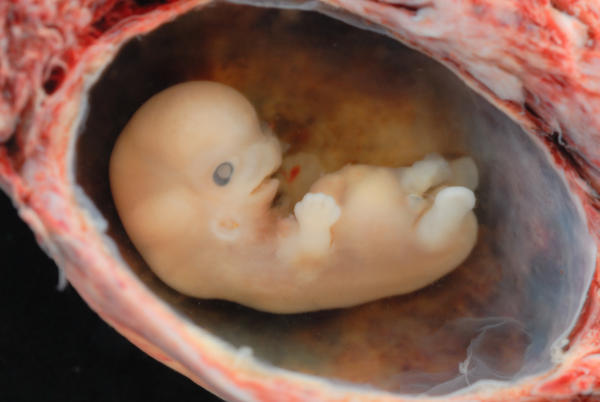 Miscarriage Chances after Seeing Heartbeat | MD-Health.com
Miscarriage Chances after Seeing Heartbeat | MD-Health.com Likelihood of miscarriage after heartbeat at 8 weeks | Mumsnet
Likelihood of miscarriage after heartbeat at 8 weeks | Mumsnet Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science Miscarriage after Heartbeat: Risks After You See Heartbeat
Miscarriage after Heartbeat: Risks After You See Heartbeat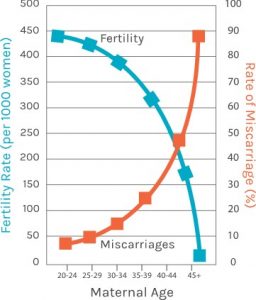 Miscarriages: How Common Are They When You Use Donor Egg?
Miscarriages: How Common Are They When You Use Donor Egg? How Common is Miscarriage After Seeing a Heartbeat?
How Common is Miscarriage After Seeing a Heartbeat? Two miscarriages and now 8 weeks 3 days - November 2019 Babies ...
Two miscarriages and now 8 weeks 3 days - November 2019 Babies ... Miscarriage Statistics by Week and What Affects Your Risk!
Miscarriage Statistics by Week and What Affects Your Risk!:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pregnancy-test-result-693305549-5bc0c4f6c9e77c00515c6d5a.jpg) 13 Milestones for Your Pregnancy After Miscarriage
13 Milestones for Your Pregnancy After Miscarriage How Common Is A Missed Miscarriage And What Causes It?
How Common Is A Missed Miscarriage And What Causes It? Pregnancy, the hardest race of all: 'If miscarriage is so common ...
Pregnancy, the hardest race of all: 'If miscarriage is so common ... Miscarriage after Heartbeat: Risks After You See Heartbeat
Miscarriage after Heartbeat: Risks After You See Heartbeat Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics
Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's
Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science
Lies, Damned Lies, and Miscarriage Statistics | Expecting Science Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's
Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's No Heartbeat at 6 Weeks Ultrasound - FAQs
No Heartbeat at 6 Weeks Ultrasound - FAQs:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/no-fetal-heartbeat-on-early-ultrasound-2371357-finalv2-ct-3225afa8cdb242e9b99726bfbaad6f58.png) What No Fetal Heartbeat on an Early Ultrasound Means
What No Fetal Heartbeat on an Early Ultrasound Means What Are The Chances (Risk) Of Miscarriage By Week? | Science Trends
What Are The Chances (Risk) Of Miscarriage By Week? | Science Trends My Twelve Week Miscarriage Story — The Functional Bump
My Twelve Week Miscarriage Story — The Functional Bump How to tell you're having a miscarriage: signs and symptoms
How to tell you're having a miscarriage: signs and symptoms Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks
Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks When Does the Chance of Miscarriage Drop?
When Does the Chance of Miscarriage Drop? Why I'm shouting about my miscarriage
Why I'm shouting about my miscarriage Doctors advised to wait longer before diagnosing miscarriages ...
Doctors advised to wait longer before diagnosing miscarriages ... Risk of miscarriage by week. ???? Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes ...
Risk of miscarriage by week. ???? Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes ... Pregnancy announcement - June 2020 Babies | Forums | What to Expect
Pregnancy announcement - June 2020 Babies | Forums | What to Expect No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF
No, I'm Not 'Lucky' Because I Had a Miscarriage at 6 Weeks | SELF Heartbeat bill - Wikipedia
Heartbeat bill - Wikipedia Your Chances of Miscarriage During Pregnancy | Parents
Your Chances of Miscarriage During Pregnancy | Parents Missed Miscarriage: Can My Unborn Baby's Heartbeat Return? - everymum
Missed Miscarriage: Can My Unborn Baby's Heartbeat Return? - everymum Risks of Miscarriage Even After You See Heartbeat - New Kids Center
Risks of Miscarriage Even After You See Heartbeat - New Kids Center ▷ Missed miscarriage - Everything you need to know | Adia
▷ Missed miscarriage - Everything you need to know | Adia When Can You Hear Baby's Heartbeat?
When Can You Hear Baby's Heartbeat? Will the chances of miscarriage decrease after seeing my baby's ...
Will the chances of miscarriage decrease after seeing my baby's ... I'm sorry, there's no heartbeat': I thought it was my fault we ...
I'm sorry, there's no heartbeat': I thought it was my fault we ... 5 women share what it's like to have a miscarriage | GMA
5 women share what it's like to have a miscarriage | GMA Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's
Miscarriage statistics | Tommy's 6 Weeks and We Have a Heartbeat!!!!!! | Laughter & Love Photography
6 Weeks and We Have a Heartbeat!!!!!! | Laughter & Love Photography Study: Viable pregnancies may be getting misdiagnosed as ...
Study: Viable pregnancies may be getting misdiagnosed as ...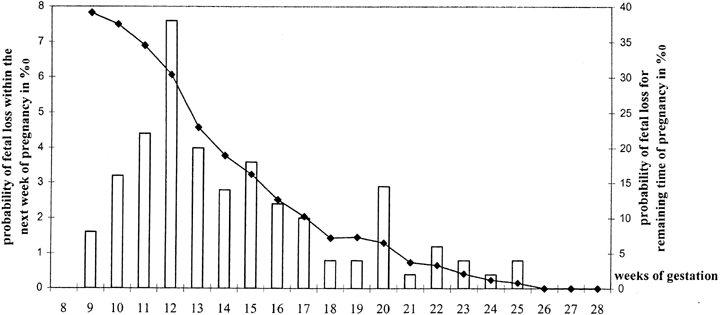 Genetic and Nongenetic Causes of Pregnancy Loss | GLOWM
Genetic and Nongenetic Causes of Pregnancy Loss | GLOWM:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ultrasound-scan-131992692-58b5efd95f9b5860461fbd74.jpg) Miscarriage After Detecting a Heartbeat on Ultrasound
Miscarriage After Detecting a Heartbeat on Ultrasound Is it true 8 weeks is a pinnacle week? - BabyCenter
Is it true 8 weeks is a pinnacle week? - BabyCenter
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar