 Blood pressure chart: Ranges, hypertension, and more
Blood pressure chart: Ranges, hypertension, and moreBlood pressure is the pressure of blood against the walls of blood vessels each time the heart contracts (squeezes) to pump blood through your body (see FAQ123). High blood pressure is also called hypertension. Hypertension can cause health problems. During pregnancy, severe or uncontrolled hypertension can cause complications for you and your fetus.
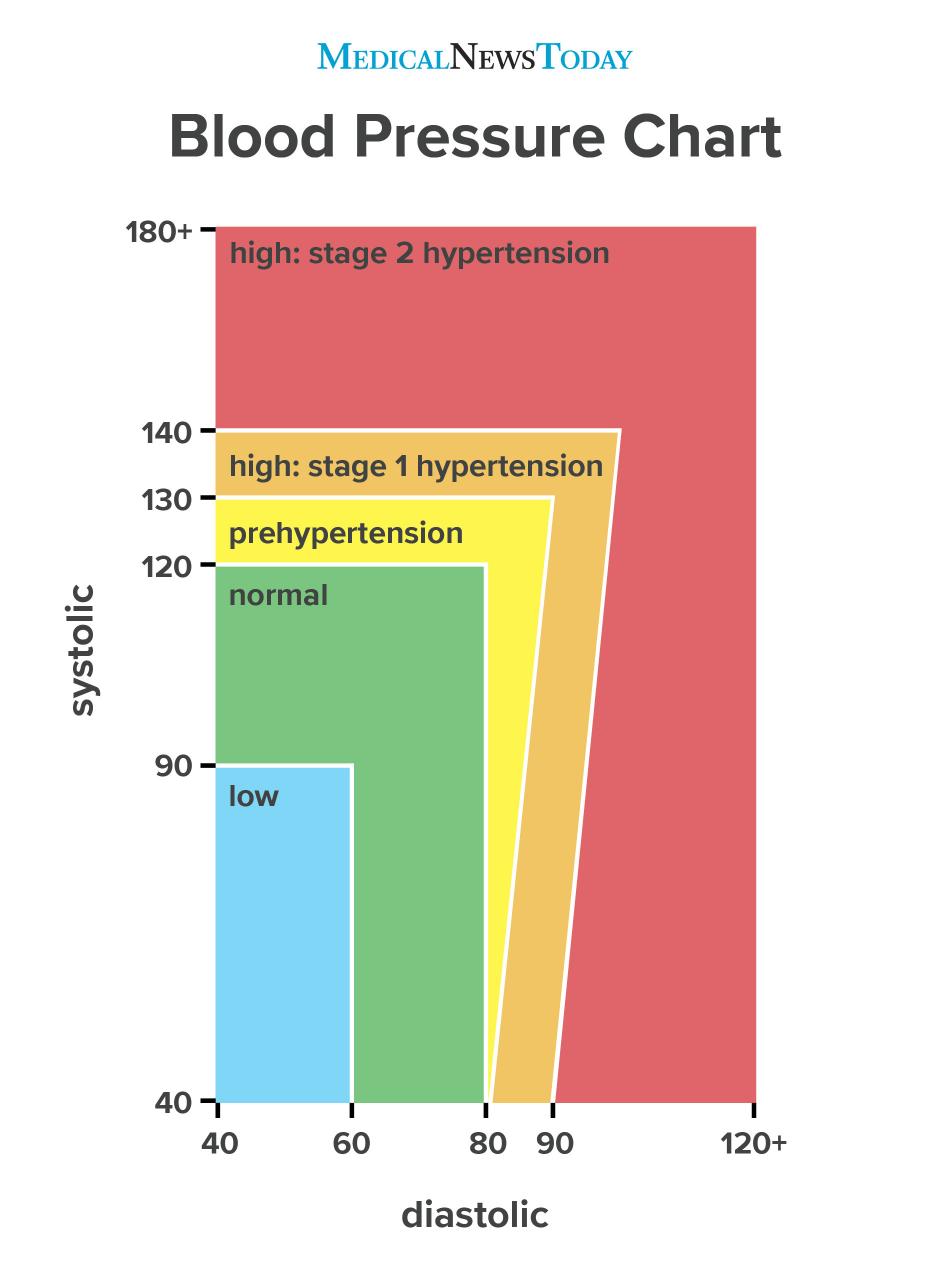
Chronic hypertension is high blood pressure that was present before you become pregnant or that occurred in the first half (before 20 weeks) of your pregnancy. Guidelines for blood pressure are as follows:
Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that first occurs after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Although gestational hypertension usually disappears after childbirth, may increase the risk of developing hypertension in the future.
High blood pressure during pregnancy can put extra pressure on the heart and kidneys and may increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, and stroke. Other possible complications include the following:
Your blood pressure will be closely monitored during pregnancy. You may need to monitor your blood pressure at home. Ultrasound exams can be done during pregnancy to track the growth of your fetus. If the growth problem is suspected, you may have additional tests that monitor the health of the fetus. This testing usually begins in the third trimester of pregnancy.
If your hypertension is mild, your blood pressure may remain as it is or even return to normal during pregnancy, and medications you may be stopped or the dose decreases. If you have severe hypertension or have health problems associated with hypertension, you might need to start or continue taking blood pressure medications during pregnancy.
Pre-eclampsia is a serious blood pressure disorder that can affect any organ in the body of a woman. A woman has preeclampsia when she had high blood pressure and other signs that their organ systems are not working normally. One of these signs is proteinuria (an abnormal amount of protein in the urine). A woman with preeclampsia whose condition is deteriorating will develop signs and symptoms known as "feature that severe." These include a low number of platelets in the blood, abnormal kidney or liver function during upper abdominal pain, changes in vision, fluid in the lungs, or severe headache. Very high blood pressure reading is also regarded as a serious feature.
This usually occurs after 20 weeks of pregnancy, usually in the third trimester. When it occurs before 34 weeks of pregnancy, it is called early-onset preeclampsia. It can also occur in the postpartum period.
It is not clear why some women develop preeclampsia. Doctors refer medium risk and high risk of preeclampsia. Risk factors for high-risk women, including
a risk factor for women who are at risk of moderate including
If preeclampsia during pregnancy, your baby may need to be delivered immediately, even if he or she is not an adult , Premature babies have an increased risk of serious complications. Some of the complications of premature lasts a lifetime and require ongoing medical care. Babies born very early can also die.
Women who had preeclampsia-especially those whose babies were born prematurely-have an increased risk of future cardiovascular disease and renal disease, including heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure. Preeclampsia once increases the risk of having again in future pregnancies. Preeclampsia can cause seizures, a condition called eclampsia. It can also lead to HELLP syndrome.
HELLP stands for hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. In this condition, red blood cells are damaged or destroyed, impaired blood clotting, and heart can bleed internally, causing chest or abdominal pain. HELLP syndrome is a medical emergency. Women can die from HELLP syndrome or have lifelong health problems as a result.
Management gestational hypertension mild or preeclampsia without features that are severe can occur either at the hospital or outpatient (you can stay at home with close monitoring by your obstetrician-gynecologist (ob-gyn) or a health care professional other). You may be asked to keep track of your baby's movements to perform everyday kick count and to measure your blood pressure at home. You will need to see your ob-gyn or other health professional at least weekly and sometimes twice a week. Once you reach 37 weekspregnancy, it may be recommended that you have your baby. If the test results indicate that the baby is not doing well, you may need to have a baby before.
Preeclampsia with heavy features usually hospitalized. If you are at least 34 weeks pregnant, is often recommended that you have your baby as soon as your condition is stable. If you are less than 34 weeks pregnant and your condition is stable, it is possible to wait to give your baby. Corticosteroids may be given to help the fetal lungs mature, and you will most likely be given medication to help reduce your blood pressure and to help prevent seizures. If your condition worsens or the baby's condition, prompt delivery will be needed.
Prevention involves identifying whether you have risk factors for preeclampsia and take steps to address these factors. If you have hypertension and are planning a pregnancy, see your ob-gyn or other health professional for a checkup before pregnancy to determine if your hypertension is under control and whether it has affected your health. If you are overweight, weight loss is usually recommended before pregnancy. If you have a medical condition, such as diabetes, it is usually recommended that your condition is well controlled before you get pregnant
Body Mass Index (BMI) :. A number calculated from height and weight. BMI is used to determine whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese
Cardiovascular Disease :. Heart and blood vessel disease.
Caesar Birth: Birth of a fetus from the uterus through an incision (cut) made in the woman's abdomen.
Chronic Hypertension: Blood pressure higher than normal for a person's age, sex and physical condition.
Complications: The disease or condition that occurs as a result of disease or other conditions. An example is pneumonia that occurs as a result of the flu. A complication can also occur as a result of conditions such as pregnancy. Examples of complications of pregnancy of preterm labor.
Corticosteroids: Drugs given to arthritis or other medical conditions. These drugs are also given to help the fetal lungs mature before birth.
Diabetes Mellitus: A condition in which blood sugar levels are too high.
Eclampsia: Seizures occur in pregnancy or after pregnancy is associated with high blood pressure.
Fetal Growth Restriction: A condition in which the fetus weighs estimated that less than 90% of other fetal same gestational age.
Fetus :. Stage of human development beyond 8 weeks was completed after fertilization
Gestational Hypertension :. High blood pressure is diagnosed after 20 weeks of pregnancy
HELLP Syndrome: A type of severe pre-eclampsia; HELLP stands for hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count
Hemolysis :. Destruction of red blood cells
High Blood Pressure :. Blood pressure above normal levels. Also called hypertension
Hypertension: High blood pressure ..
Kick Count :. A record kept during late gestation of the number of times the moving fetus during certain time periods
Kidney organ that filters the blood into the waste remove the urine
kidney disease: A general term for diseases affect how the kidneys function
liver Enzymes ..: chemicals made by liver cells. High levels of liver enzymes may suggest liver damage
Lupus :. An autoimmune disorder that affects the connective tissue in the body. The disorder can lead to arthritis, kidney disease, heart disease, blood disorders, and complications during pregnancy. Also called systemic lupus erythematosus or SLE
Nutrition :. Nourishing substances found in food, such as vitamins and minerals
Obstetrics-Gynecology (Ob-Gyn) :. A doctor with special training. education and health of women
Oxygen: An element that we breathe to sustain life
Placenta: .. An organ that provides nutrients and taking waste from the fetus
placenta abruption :. A condition in which the placenta begins to separate from the fetus before birth iuterus
The platelets: small cells found in the blood that help to stop bleeding
Postpartum :. related to the weeks after the birth of the child
Preeclampsia: a disorder that can occur during pregnancy or after childbirth in which there is high blood pressure and other signs of organ injury. These signs include abnormal amount of protein in the urine, low number of platelets, abnormal kidney or liver function during upper abdominal pain, fluid in the lungs, or severe headaches or changes in vision.
Proteinuria: presence of abnormal amounts of protein in the urine
Stroke :. a sudden interruption of blood flow to all or part of the brain, caused by a blockage or burst blood vessel in the brain. Stroke often causes loss of consciousness and temporary or permanent paralysis
Trimester :. 3 months of pregnancy. This may be the first, second, or third
Ultrasound Exam :. A test in which sound waves are used to examine the inside of the body
FAQ034 :. This information is designed as an educational aid for patients and sets forth current information and opinions related to women's health. It is not intended as a statement of the standard of care, is not made up of all the appropriate care or treatment methods. It is not a substitute for independent professional assessment of this treating clinician. Please check for updates on to ensure accuracy.
Copyright October 2019 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
FAQs Related
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 409 12th Street SW, Washington, DC 20024-2188 Mailing Address: PO Box 96920, Washington, DC 20024-9998
 Blood Pressure Readings Explained
Blood Pressure Readings Explained Blood pressure levels during pregnancy (n 5 8236) a | Download Table
Blood pressure levels during pregnancy (n 5 8236) a | Download Table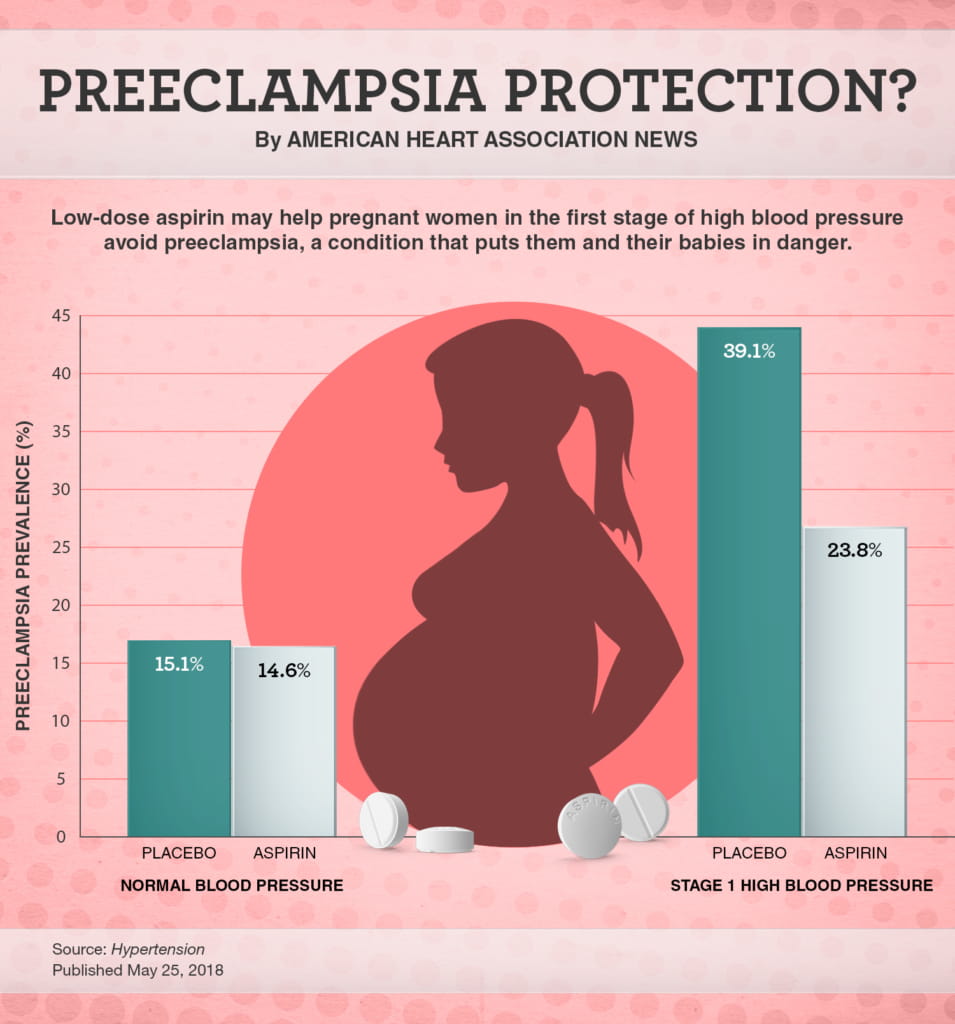 Low-dose aspirin could help pregnant women with high blood ...
Low-dose aspirin could help pregnant women with high blood ...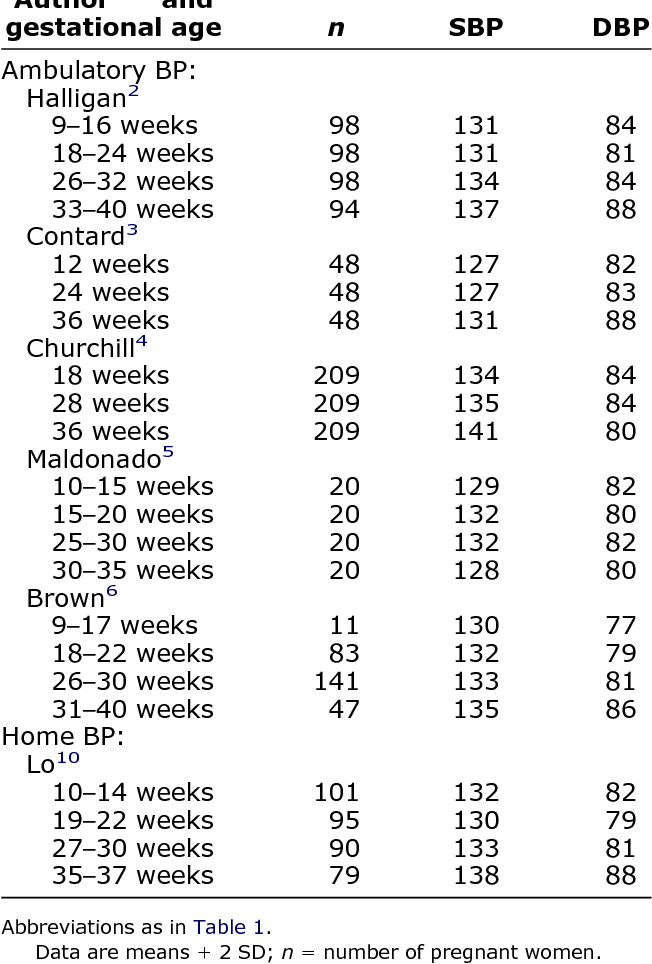 Table 2 from Home blood pressure during normal pregnancy ...
Table 2 from Home blood pressure during normal pregnancy ... Blood pressure levels during pregnancy (n 5 8236) a | Download Table
Blood pressure levels during pregnancy (n 5 8236) a | Download Table A blood pressure chart for adults showing high, low and normal ...
A blood pressure chart for adults showing high, low and normal ... Blood pressure course during pregnancy stratified for women with ...
Blood pressure course during pregnancy stratified for women with ... Maternal blood pressure in pregnancy, birth weight, and perinatal ...
Maternal blood pressure in pregnancy, birth weight, and perinatal ... Cardiovascular Physiology of Pregnancy | Circulation
Cardiovascular Physiology of Pregnancy | Circulation Blood Pressure Chart By Age - Understand Your Normal Range
Blood Pressure Chart By Age - Understand Your Normal Range Spiral Arterial Remodeling Is Not Essential for Normal Blood ...
Spiral Arterial Remodeling Is Not Essential for Normal Blood ... If 110/70 is normal blood pressure, what is the normal range for ...
If 110/70 is normal blood pressure, what is the normal range for ... preeclampsia blood pressure chart - Catan.vtngcf.org
preeclampsia blood pressure chart - Catan.vtngcf.org Pre-Eclampsia and Hypertensive Disease in Pregnancy
Pre-Eclampsia and Hypertensive Disease in Pregnancy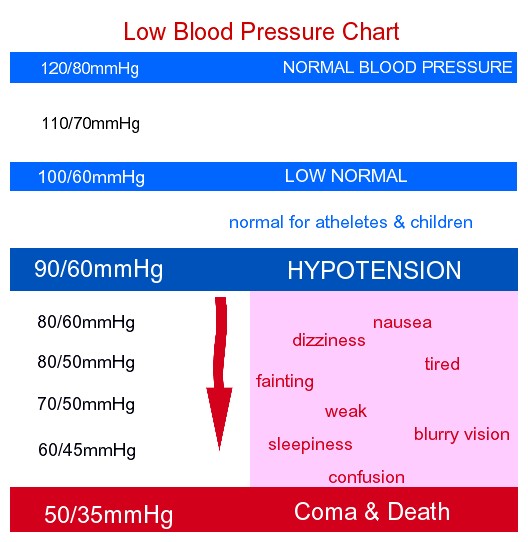 Low Blood Pressure Chart - | For Women | By Age | For men | During ...
Low Blood Pressure Chart - | For Women | By Age | For men | During ... Heart rate and blood pressure changes during pregnancy are less ...
Heart rate and blood pressure changes during pregnancy are less ... Association between calcium intake, parathormone levels and blood ...
Association between calcium intake, parathormone levels and blood ... Normal Blood Pressure Chart | Blood pressure remedies, Blood ...
Normal Blood Pressure Chart | Blood pressure remedies, Blood ...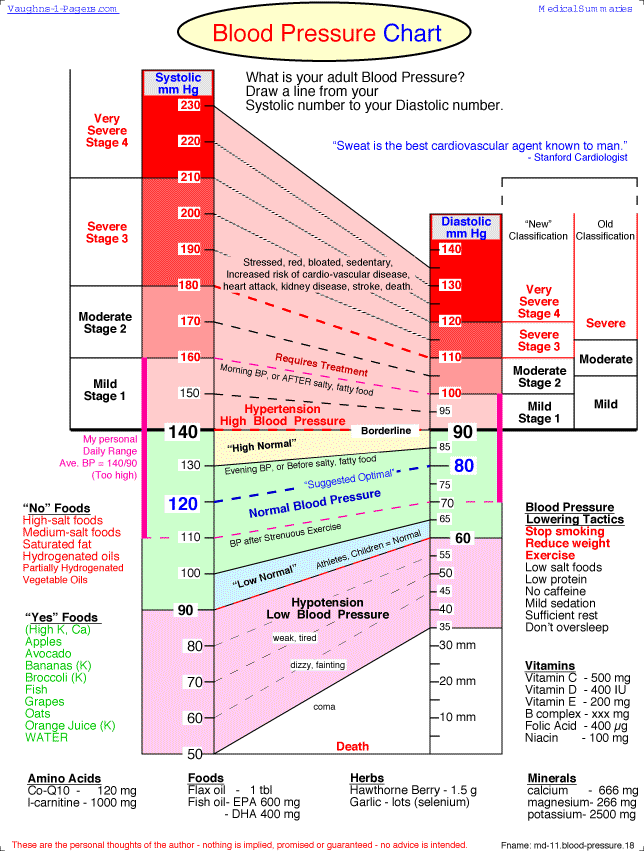 Useful info for blood pressure
Useful info for blood pressure Trend of blood pressure changes in normal pregnancy. Y-axis: Mean ...
Trend of blood pressure changes in normal pregnancy. Y-axis: Mean ... Blood pressure in pregnancy - is dangerous or not | Health Care ...
Blood pressure in pregnancy - is dangerous or not | Health Care ... Making sense of preeclampsia tests
Making sense of preeclampsia tests High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) | Texas Heart Institute
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) | Texas Heart Institute Low blood pressure during pregnancy: Causes and remedies
Low blood pressure during pregnancy: Causes and remedies Preeclampsia and High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy - ACOG
Preeclampsia and High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy - ACOG Hypertension in Pregnancy
Hypertension in Pregnancy These High Blood Pressure Treatments Really Work | Blood pressure ...
These High Blood Pressure Treatments Really Work | Blood pressure ... 75 Good Blood Pressure For Pregnancy
75 Good Blood Pressure For Pregnancy Table 1 from Home blood pressure during normal pregnancy ...
Table 1 from Home blood pressure during normal pregnancy ... High Blood Pressure | Rehabilitate Your Heart
High Blood Pressure | Rehabilitate Your Heart Birth Injury Attorneys | Mismanaged Preeclampsia
Birth Injury Attorneys | Mismanaged Preeclampsia Blood Pressure Patterns in Normal Pregnancy, Gestational ...
Blood Pressure Patterns in Normal Pregnancy, Gestational ... Hypertension Canada's 2018 Guidelines for the Management of ...
Hypertension Canada's 2018 Guidelines for the Management of ... Abnormal Blood Pressure Levels in Pregnancy
Abnormal Blood Pressure Levels in Pregnancy Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy - ppt download
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy - ppt download The line chart showing the transition of diastolic blood pressure ...
The line chart showing the transition of diastolic blood pressure ... Chronic high blood pressure in pregnancy | BabyCenter
Chronic high blood pressure in pregnancy | BabyCenter Blood pressure in pregnancy - BabyCentre UK
Blood pressure in pregnancy - BabyCentre UK What Causes High Blood Pressure: The Unexpected And The Strange
What Causes High Blood Pressure: The Unexpected And The Strange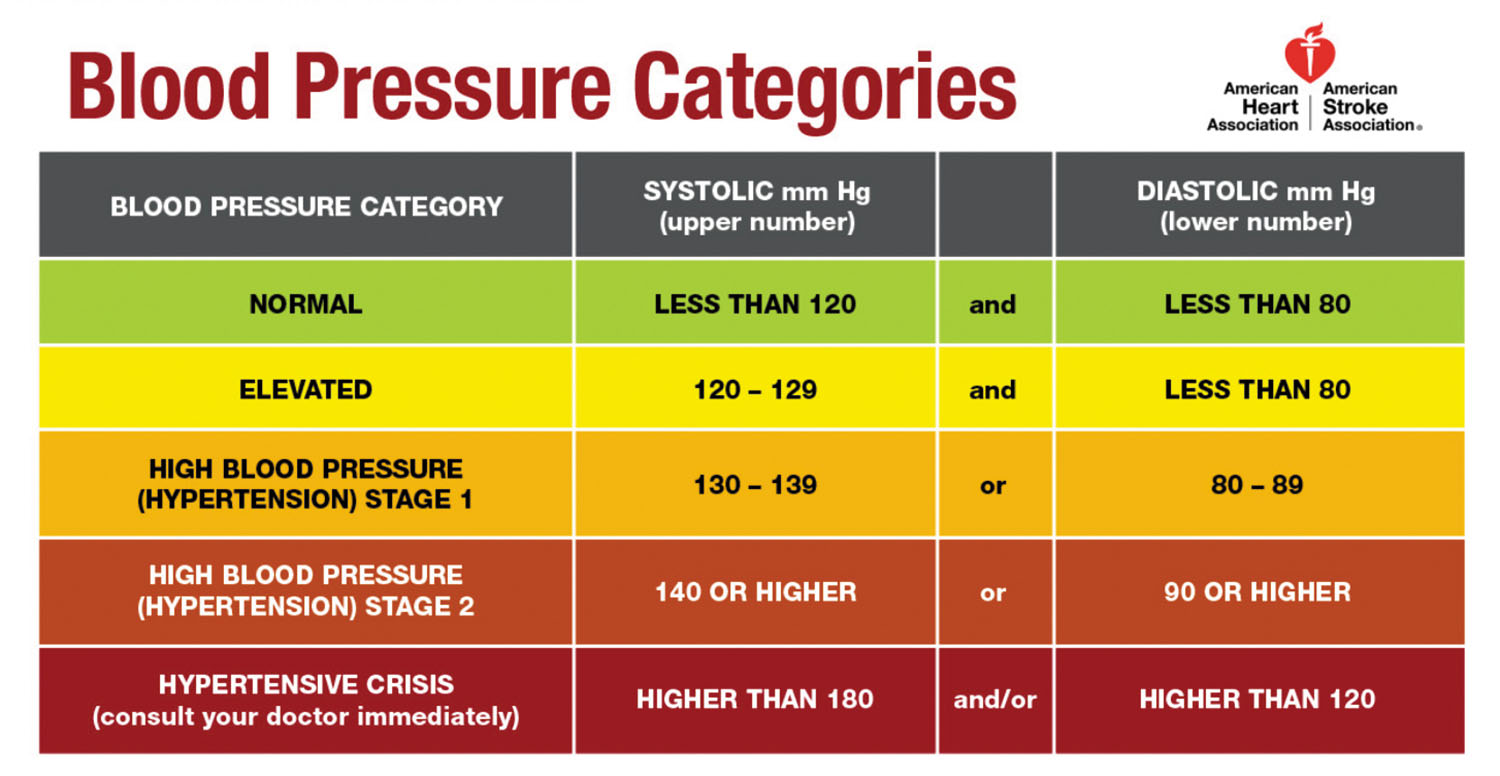 Reading the new blood pressure guidelines - Harvard Health
Reading the new blood pressure guidelines - Harvard Health preeclampsia blood pressure chart - Catan.vtngcf.org
preeclampsia blood pressure chart - Catan.vtngcf.org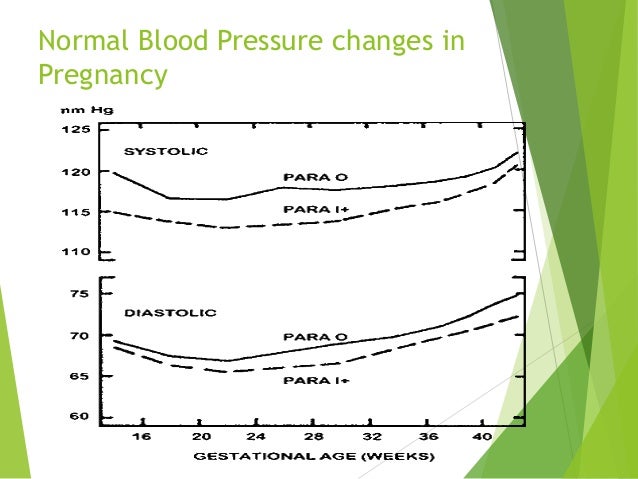 Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy Normal Values (Section 8) - High-Risk Pregnancy
Normal Values (Section 8) - High-Risk Pregnancy Hypertension during pregnancy Dr. Yosra Tahir Ninevah College of ...
Hypertension during pregnancy Dr. Yosra Tahir Ninevah College of ... Association between calcium intake, parathormone levels and blood ...
Association between calcium intake, parathormone levels and blood ... Gestational hypertension – Pregnancy Info
Gestational hypertension – Pregnancy Info Trend of blood pressure changes in normal pregnancy. Y-axis: Mean ...
Trend of blood pressure changes in normal pregnancy. Y-axis: Mean ...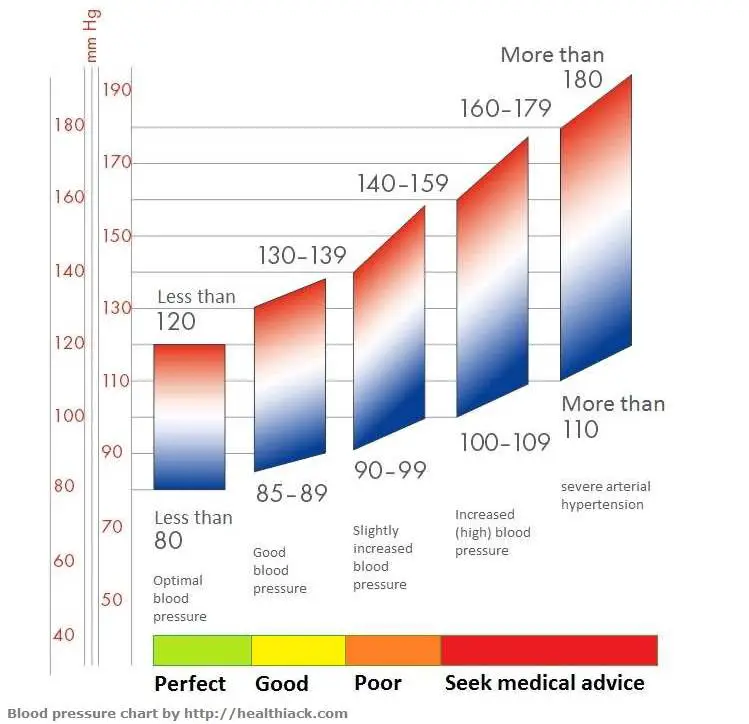 Blood pressure, a health indicator
Blood pressure, a health indicator High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy | cdc.gov
High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy | cdc.gov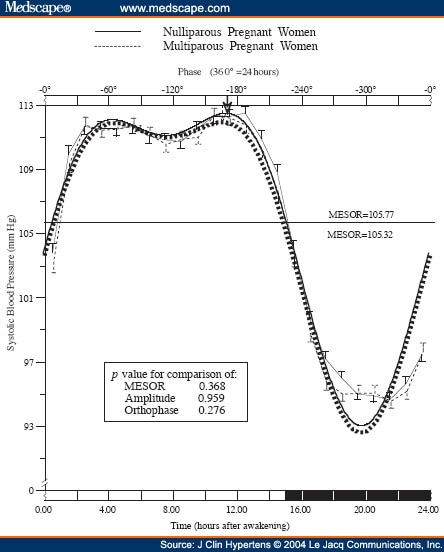 Circadian Blood Pressure Variability as a Function of Parity
Circadian Blood Pressure Variability as a Function of Parity Normal Blood Pressure Level For Men Fasting Blood Sugar In ...
Normal Blood Pressure Level For Men Fasting Blood Sugar In ...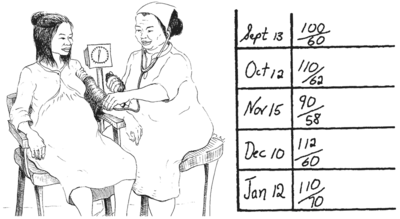 Check Health Signs - Hesperian Health Guides
Check Health Signs - Hesperian Health Guides High normal blood pressure in early pregnancy also contribute to ...
High normal blood pressure in early pregnancy also contribute to ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar