:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-causes-second-trimester-miscarriages-2371490_final-924d725c102c49a1b4f34d9003f4cef0.png) Reasons for Miscarriage in the Second Trimester
Reasons for Miscarriage in the Second Trimestersecond-trimester pregnancy loss can result from very premature births (such as spontaneous abortion in the second trimester) or fetal death (called fetal death). Approximately 2-3% of pregnancies are lost in the second trimester, a much lower level than in the first trimester. After pregnancy up to about 20 weeks of pregnancy, less than 0.5% will end in fetal death.
A current loss in pregnancy is most often experience hard and sad. Many friends and family know you are pregnant. What are you doing? What do you say? For most women and their partners, the grieving process is no different than losing someone who has been in your life for some time. You often have hopes and dreams of your child before the child was born, and loss of pregnancy in the second or third trimester is certainly a loss for the family.
Our specialists can evaluate you quickly in an office setting. Each testing laboratory or ultrasound examination needs to be done can be done easily and comfortably. We did our own ultrasound examination in the office and can share the results with you soon. Treatment of second trimester losses are very different from the early miscarriage, and our specialists can provide all the options for you and your family. We understand that the current loss requires both emotional and medical support. We are happy to review all treatment options but also know that you may need some time. It is also important for you to know that the death of a fetus in the second trimester was not a medical emergency so that treatment is not promptly given.
If you experience very heavy vaginal bleeding or feel very sick, you should go to the Emergency Room to see our doctor.
Most women less than 20 weeks gestation did not notice any symptoms of fetal death.
The test is used to check for fetal death in the second trimester is an ultrasound to see if the baby is moving and growing. fetal death was diagnosed when ultrasound examination showed no fetal heart activity.
The cause of losses in the second trimester of pregnancy is very different from the early loss of pregnancy. There are medical conditions that increase the risk for the insufficiency of the cervix or preterm birth before viability include:
There are also several medical conditions related to the death of the fetus in the second trimester include:
Experts in UC Davis Health will review with you what the test is indicated to help learn more about why the second trimester losses occur. Although testing is available, about half of the time there is no reason identified for the second trimester losses. We can work with you to figure out what can help with future pregnancies or to learn more about medical problems that are important to your future.
It is generally not safe for a woman to wait for pregnancy to express themselves with second trimester losses. There is a high chance of having significant bleeding when pregnancy in the second trimester provides its own at home. In the case of fetal death, fetal death who had been in utero during 4 weeks can cause changes in the coagulation system of the body. These changes can put a woman at a much higher chance of significant bleeding if he waited for a long time after the death of the fetus to convey pregnancy.
Our doctors are committed to providing all the treatment options available. Tests to find out the cause of pregnancy loss can be done without method woman again opted for termination.
We understand that the loss of the second trimester is an emotional and stressful time and we want to make sure that the emotional needs of you and your family are met as well. We understand this is a time that you need support and we are sensitive to your wishes for a memorable and religious preference. We will discuss this issue with you prior to treatment.
When the diagnosis of fetal death in the second or third trimester were made, the options include:
Induction of Labor: This treatment uses drugs to cause the uterus to go into labor. For women with a pregnancy beyond 24 weeks, it is often the only choice. If you choose this option, you will be in the Labor and Delivery Unit at UC Davis Medical Center and will have all the same pain treatment available to you as a woman who is naturally in labor (such as IV or epidural pain medication). treatme thatnt typically starts with swallowing pills to make the uterus more sensitive to drugs to induce labor. About 24 hours later, you are admitted to Labor and Delivery Unit and shall medication (tablet) is inserted into the vagina every few hours to the cause of labor. Sometimes, women take the drug intravenously to also help workers get started. It may take 1-2 days for the uterus to go into labor and delivery to be complete. Up to 5% of women in the second trimester did not go into labor and require surgical evacuation.
Your doctor will be able to explain in more detail about the pros and cons of each treatment.
Bleeding may continue for several weeks after the induction of labor, but tend to be much lighter with surgical evacuation. Bleeding can change color from bright red to pink or brown. Lowering abdominal cramps within a few days after treatment are also common. You should contact a doctor immediately if bleeding becomes heavier than the lighter over time, if fever develops, or if vaginal discharge or vaginal odor strange or unpleasant happens. Avoid sexual intercourse, douching, or using tampons for one week. Routine activities can be resumed immediately, based on how you feel. What is important, if you want to postpone pregnancy, it will be important to initiate effective contraceptive methods
Q :. What cervical insufficiency? A: This diagnosis is made when a woman has a dilation of the cervix during the second trimester without having contractions or other signs of infection of the uterus. Several studies have shown that some types of surgery performed when women have advanced pre-cancerous changes in the cervix may increase the risk of cervical insufficiency. These operations include conization of the cervix (also known as the "cone biopsy") or if the patient has had a LEEP procedure a few. With this operation, part of the cervix is removed to get rid of pre-cancerous changes. Having this procedure increases the risk of second trimester losses of about 1%. In women who have this type of procedure, the chance of having cervical insufficiency is about 1.5% .Q: What treatments are available if one of the tests showed I had a medical problem that increases the likelihood of second trimester losses? A: Our specialists will work with you to maximize your health status before you try to conceive again. For some women, this means that the treatment of thyroid conditions, improve diabetes control, or change the drugs used for chronic diseases. Some conditions may require blood thinners such as aspirin or injectable drugs should be started at the beginning of the next pregnancy (after normal pregnancy visible with ultrasound examination early) .Q: On my last pregnancy, I do not get genetic testing and have a second trimester deaths associated with a genetic disorder , What genetic tests available for subsequent pregnancies to help find out if the pregnancy is normal so that I could learn early if genetically normal pregnancy? A: It will be important to meet with a genetic counselor, if possible, before the next pregnancy, which can also be reviewing the details of the test are available. The counselor can also talk to you about your family's history and history to ensure there are no medical problems genetic or familial missed. There are different tests, all of which can be done early in pregnancy, depending on what is right for you. Screening for some of the most common chromosome abnormality only from the blood (called NIPT or non-invasive prenatal testing). First-trimester screening can be done between 11 and 14 weeks involving blood tests and ultrasound. In some situations, chorionic villus sampling (placental biopsy) or expanded prenatal screening may be indicated. Our specialist and genetic counselor can work with you and your family to help you understand all these tests and find out what the right approach to you.Q: After losing the second trimester, how long should I wait before I try to get pregnant again? A: There is really no information available to indicate either the absolute right answer to that question. First, it may take a month or two to have completed testing to help figure out why you are having second trimester losses. We know that it takes some time for your uterus and your body to return to normal. Experts at UC Davis are usually advised to wait at least 3 months after losing the second trimester before trying again to get a pr, Egnant
Patients line: landing Clinician:
The staff is available to assist you Monday through Friday, 08: 00-05: 00
Stay connected with what's happening at UC Davis Health Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
4860 Y Street, Suite 2500 | Sacramento, CA 95817 | Ellison Clinic: All copyrights | | |
/what-causes-second-trimester-miscarriages-2371490_final-924d725c102c49a1b4f34d9003f4cef0.png) Reasons for Miscarriage in the Second Trimester
Reasons for Miscarriage in the Second Trimester Second Trimester Miscarriage | babyMed.com
Second Trimester Miscarriage | babyMed.com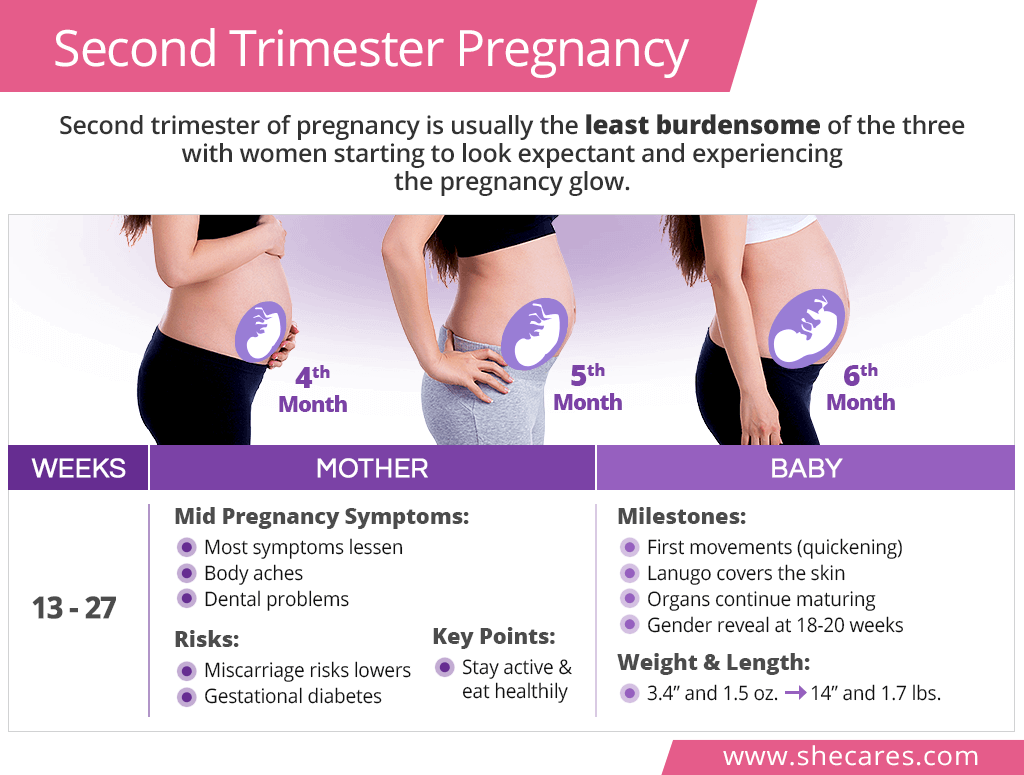 Second Trimester Pregnancy | SheCares
Second Trimester Pregnancy | SheCares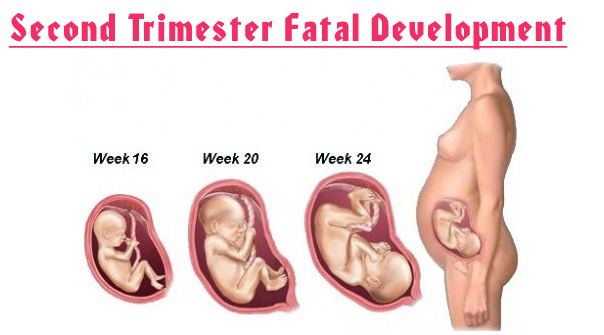 Second Trimester of Pregnancy Week By Week, Symptoms And Ultrasound
Second Trimester of Pregnancy Week By Week, Symptoms And Ultrasound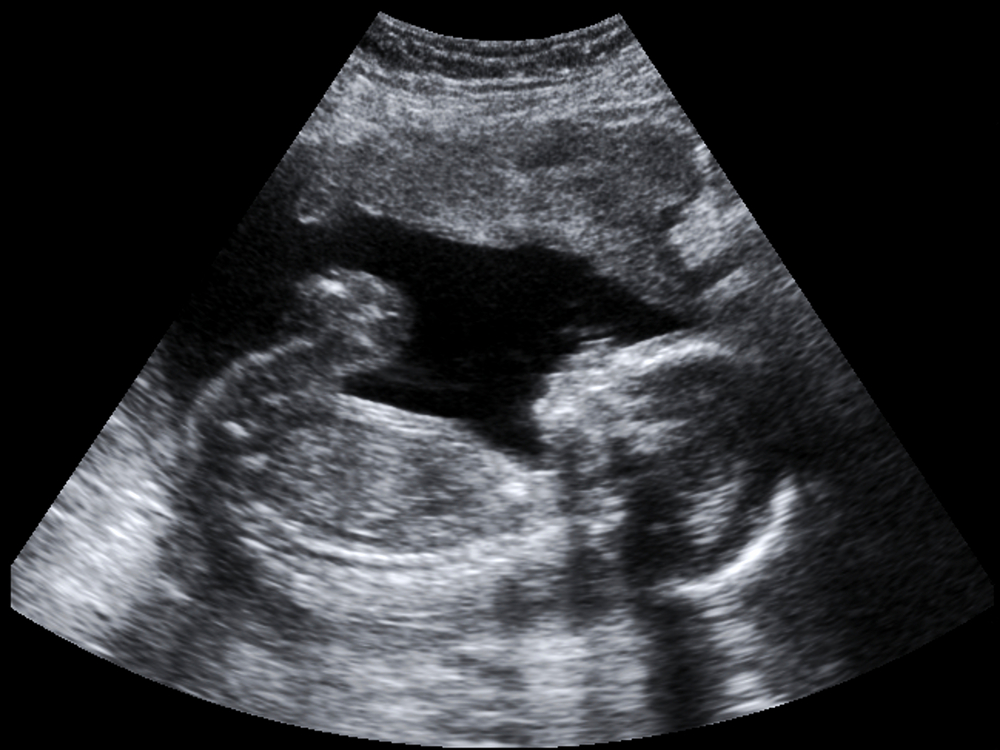 We Lost Our Baby at 17 Weeks Pregnant - Her View From Home
We Lost Our Baby at 17 Weeks Pregnant - Her View From Home Second Trimester Miscarriage Is The Worst Thing I Have Ever Been ...
Second Trimester Miscarriage Is The Worst Thing I Have Ever Been ... miscarriage signs & symptoms Archives | Siddha Spirituality For Health
miscarriage signs & symptoms Archives | Siddha Spirituality For Health Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms & Causes | Live Science
Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms & Causes | Live Science The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications
The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications CHINESE MEDICINE BRISTOL: How to have a healthy pregnancy: Second ...
CHINESE MEDICINE BRISTOL: How to have a healthy pregnancy: Second ... Second Trimester Pregnancy | SheCares
Second Trimester Pregnancy | SheCares/14-5b352ff6c9e77c003722e936.png) 14 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More
14 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications
The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications Second trimester: How much pain, bleeding, and discharge is normal?
Second trimester: How much pain, bleeding, and discharge is normal? Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis
Miscarriage without bleeding: Symptoms and diagnosis/GettyImages-487998567-59ed55a622fa3a0011bdedb1.jpg) First and Second Trimester Miscarriage Differences
First and Second Trimester Miscarriage Differences Late Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery
Late Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery The Second Trimester of My First Pregnancy | Parenting Patch
The Second Trimester of My First Pregnancy | Parenting Patch Week 16: Late Miscarriage | Parents
Week 16: Late Miscarriage | Parents The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications
The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications Second trimester OF PREGNANCY
Second trimester OF PREGNANCY How long does a miscarriage last?
How long does a miscarriage last? Miscarriage - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Miscarriage - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia/GettyImages-180463725-56b37cba3df78cf7385c9f5b.jpg) Treatment for a Second Trimester Miscarriage
Treatment for a Second Trimester Miscarriage The miscarriage: what is it? Causes, Symptoms and Treatment ...
The miscarriage: what is it? Causes, Symptoms and Treatment ... The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications
The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: Complications My Second Trimester Miscarriage... What Happened and How I'm ...
My Second Trimester Miscarriage... What Happened and How I'm ...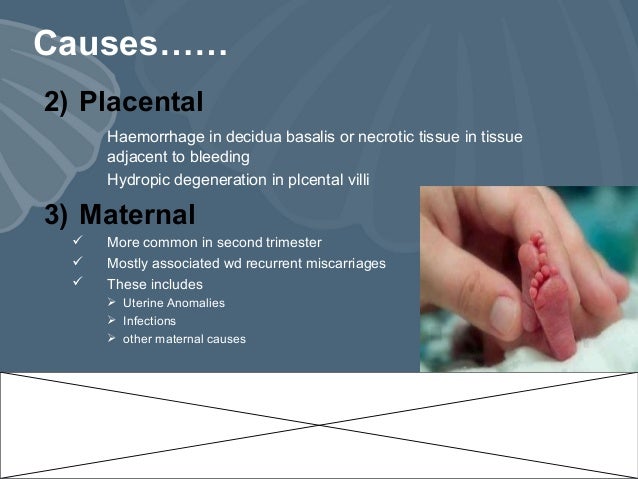 Miscarriages,,!!!
Miscarriages,,!!! 4 Things You Should Know About the Second Trimester - EverydayFamily
4 Things You Should Know About the Second Trimester - EverydayFamily Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician
Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician What Does a Miscarriage Feel Like? Symptoms at Different Stages
What Does a Miscarriage Feel Like? Symptoms at Different Stages Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics
Miscarriage rates by week: Risks and statistics/Untitled_Artwork-6f442377a59e48b9b30cc19f5cd7694b.png) Diagnosis of a Miscarriage Without Bleeding
Diagnosis of a Miscarriage Without Bleeding Pregnancy After Miscarriage: From Risks to Rainbow Babies
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: From Risks to Rainbow Babies Second trimester OF PREGNANCY
Second trimester OF PREGNANCY PDF) Fetal Pathology in Second-Trimester Miscarriages
PDF) Fetal Pathology in Second-Trimester Miscarriages Hillaria Baldwin's late miscarriage is rare -- and traumatic
Hillaria Baldwin's late miscarriage is rare -- and traumatic Miscarriage - Wikipedia
Miscarriage - Wikipedia How to Prevent Miscarriage: Is It Possible?
How to Prevent Miscarriage: Is It Possible? Missed miscarriage statistics second trimester.
Missed miscarriage statistics second trimester. Indications for and pregnancy outcomes of cervical cerclage: 11 ...
Indications for and pregnancy outcomes of cervical cerclage: 11 ... Delivering Death: Second Trimester Miscarriage
Delivering Death: Second Trimester Miscarriage![Full text] Validation of second trimester miscarriages and ... Full text] Validation of second trimester miscarriages and ...](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s85000/85107/img/Table2.jpg) Full text] Validation of second trimester miscarriages and ...
Full text] Validation of second trimester miscarriages and ... The Second Trimester - Pregnancy
The Second Trimester - Pregnancy Second trimester: weeks 13 to 28 | Tommy's
Second trimester: weeks 13 to 28 | Tommy's Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks
Miscarriage Rates by Week: Causes and Risks:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-does-an-early-miscarriage-look-like-2371235_FINAL-3bd3a25d94e24ad4823d74eef739f4e4.png) Miscarriage or Period: How to Tell the Difference
Miscarriage or Period: How to Tell the Difference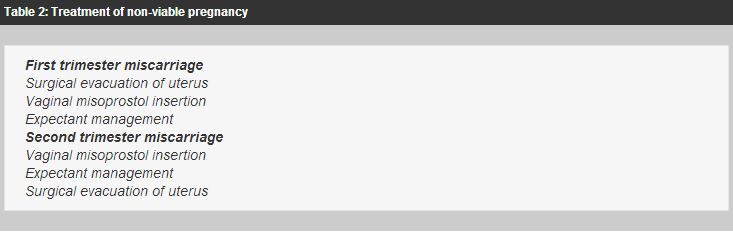 The Hong Kong Practitioner
The Hong Kong Practitioner Missed miscarriage statistics second trimester.
Missed miscarriage statistics second trimester. Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms, and Causes | babyMed.com
Miscarriage: Signs, Symptoms, and Causes | babyMed.com Second trimester miscarriage - The Miscarriage Association
Second trimester miscarriage - The Miscarriage Association Late Miscarriage – Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery - YouTube
Late Miscarriage – Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery - YouTube Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss (Chapter 25) - Obstetric Care
Second Trimester Pregnancy Loss (Chapter 25) - Obstetric Care Recurrent Miscarriage, Investigation and Treatment of Couples ...
Recurrent Miscarriage, Investigation and Treatment of Couples ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar