 3 Types Of Contractions During Pregnancy & Its Significance
3 Types Of Contractions During Pregnancy & Its SignificanceIf you are pregnant, one of the first concerns what you might like.
This information will help answer the most common questions about labor, especially if this is your first. For detailed information about delivery, see.
Some women experience signs are very different from the workforce, while others do not. No one knows what causes labor to start or when it will start, but some hormonal changes and physical can indicate the beginning of work:
The process of your baby settle down or degrade into your pelvis just before birth is called lightening. Waivers can occur a few weeks or a few hours before delivery. Because the rest of the uterus on more after lightening, you may feel the need to urinate more frequently.
Plug accumulate mucus in the cervix during pregnancy. When the cervix begins to open wider, mucus and perhaps thrown into clear, pink, or slightly bloody. Labor can be started immediately after the mucus plug is discharged or one to two weeks later.
During the contraction, it becomes hard. Between contractions, the uterus relaxes and the abdomen becomes soft. How contraction feels different for every woman, and may feel different from one pregnancy to the next. But labor contractions usually cause discomfort or pain in the back and lower abdomen, along with the pressure in the pelvis. Contraction move in wavelike motion from the top of the uterus down. Some women describe the strong contractions. Unlike contractions or false labor, true labor contractions do not stop when you change the position or relax. Although contraction may be uncomfortable, you will be able to relax between contractions.
Before the "true" labor begins, you may have to "false" labor pains, also known as Braxton Hicks contractions. irregular contractions of the uterus is normal and may start to happen to you, although it is more common in you. They are your body's way of getting ready for the "real thing."
Braxton Hicks contractions can be described as tightening in the stomach that comes and goes. These contractions are not closer together, not increased by foot, did not increase the duration, and do not feel stronger over time as they did when you were in labor right.
To find out if you are feeling contractions are the real thing, ask yourself the following questions.
If you think you are in labor right, from time contractions. To do this, write down time each contraction started and stopped or have someone do it for you. The time between contractions including the length or duration of the contractions and minutes between contractions (called the interval).
mild contraction generally begin 15 to 20 minutes apart and last 60 to 90 seconds. Contractions became more regular until they are less than 5 minutes apart. Active labor (when you have to come to the hospital) are typically characterized by strong contractions that last 45 to 60 seconds and occur three to four minutes apart.
The first stage of labor (called the latent phase) of the most experienced in the comfort of your home. Here are some tips to help you cope:
rupture of amniotic membrane (fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby during pregnancy) may feel good as a sudden gush of fluid or liquid droplets that leak continues. This fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored. If your "water breaks," wrote down the time it happens, how much liquid is released, and what looks like a liquid, and then tell your provider. Your doctor can advise you what to do next.
Finally, keep in mind that not all women will have their water break when they are in labor. Many times the doctor will rupture the membranes in the hospital.
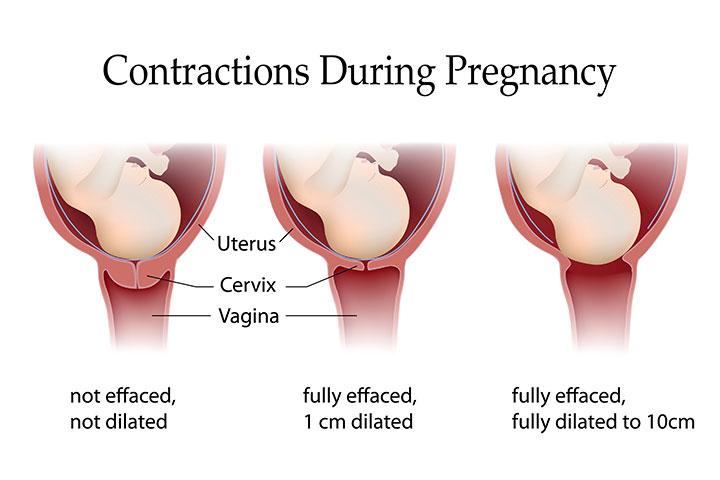
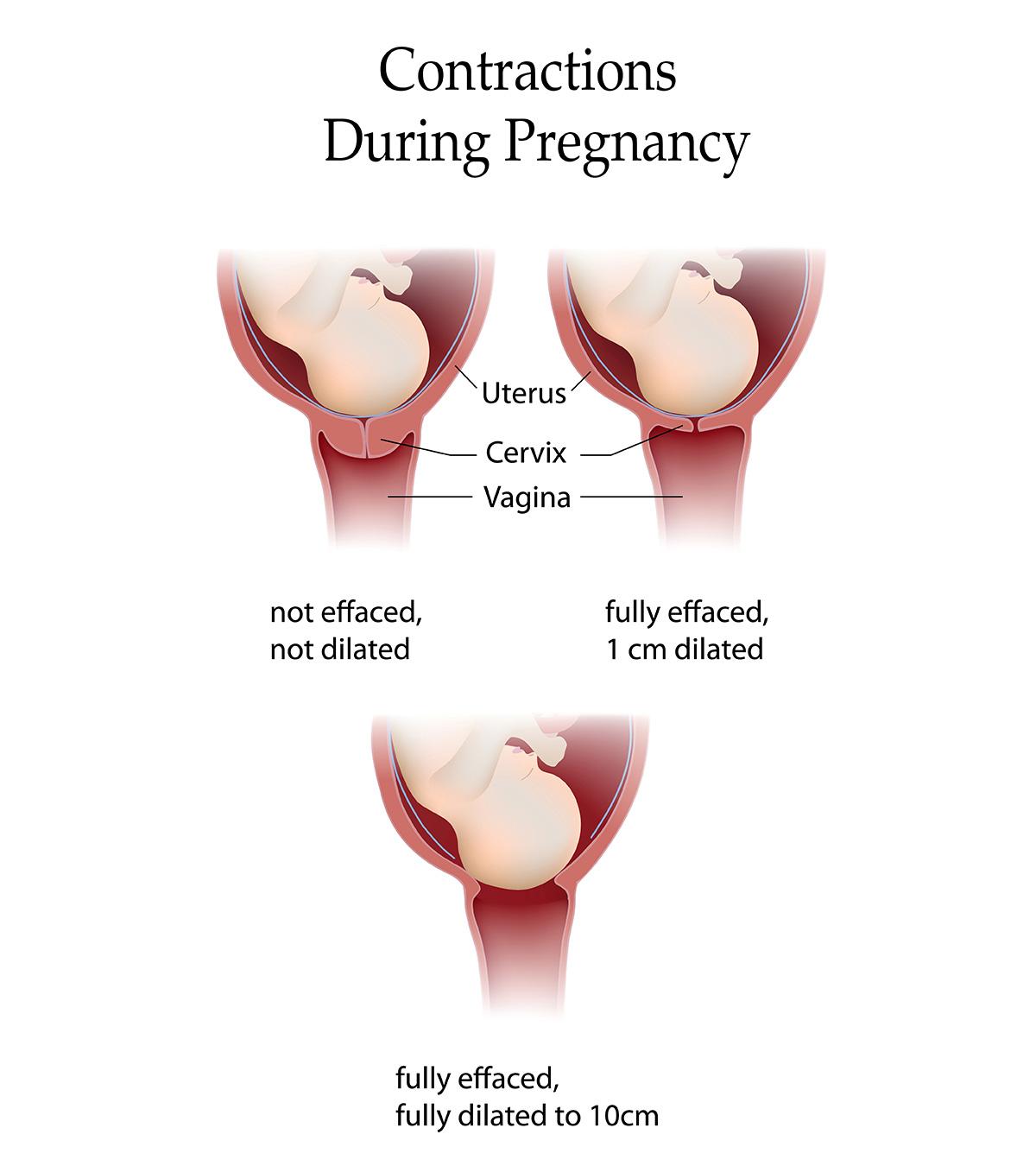
During labor, your cervix to get shorter and thinned out to stretch and open about your baby's head. The shortening and thinning of the cervix called a deletion. Your provider will be able to tell you if there are changes in the cervix during. Depletion is measured in percentages from 0% to 100%. If there is no change in the cervix, it is described as 0% eliminated. When the cervix is half the normal thickness, that is 50% eliminated. When the cervix is completely depleted, it was 100% eliminated.
and the opening of your cervix called dilation and measured in centimeters, with complete dilation are at 10 cm.
thinning and dilation is a direct result of the effective uterine contractions. Progress in labor is measured by how much the cervix has opened and thinned to allow the baby to pass through.
If you suspect you are in the workforce, contact your health care provider. Also, call:
The doctor will provide specific guidance about when you should get ready to come to the hospital
SOURCE: American Pregnancy Association ..
Pagination
© 2005 - 2019 WebMD LLC. OF.
WebMD does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
 3 Types Of Contractions During Pregnancy & Its Significance
3 Types Of Contractions During Pregnancy & Its Significance Braxton Hicks Contractions | SheCares
Braxton Hicks Contractions | SheCares True Labor False Labor Contractions Occur at Regular Contractions ...
True Labor False Labor Contractions Occur at Regular Contractions ... Braxton Hicks Contractions—Answers to Your Top Questions! | Bloomlife
Braxton Hicks Contractions—Answers to Your Top Questions! | Bloomlife Braxton Hicks Contractions: Recognizing Practice Labor (Infographic)
Braxton Hicks Contractions: Recognizing Practice Labor (Infographic) Pregnancy : A Better Understanding of Contractions
Pregnancy : A Better Understanding of Contractions Pre-Labor Signs|Early Labor Signs|Difference Between True and ...
Pre-Labor Signs|Early Labor Signs|Difference Between True and ... 4 Signs You May Be Going into Labor | UPMC HealthBeat
4 Signs You May Be Going into Labor | UPMC HealthBeat/how-to-time-contractions-2752965_v1-37cf2fed03c045d8b4652d27b9eeeff7.png) How to Time Your Contractions During Labor
How to Time Your Contractions During Labor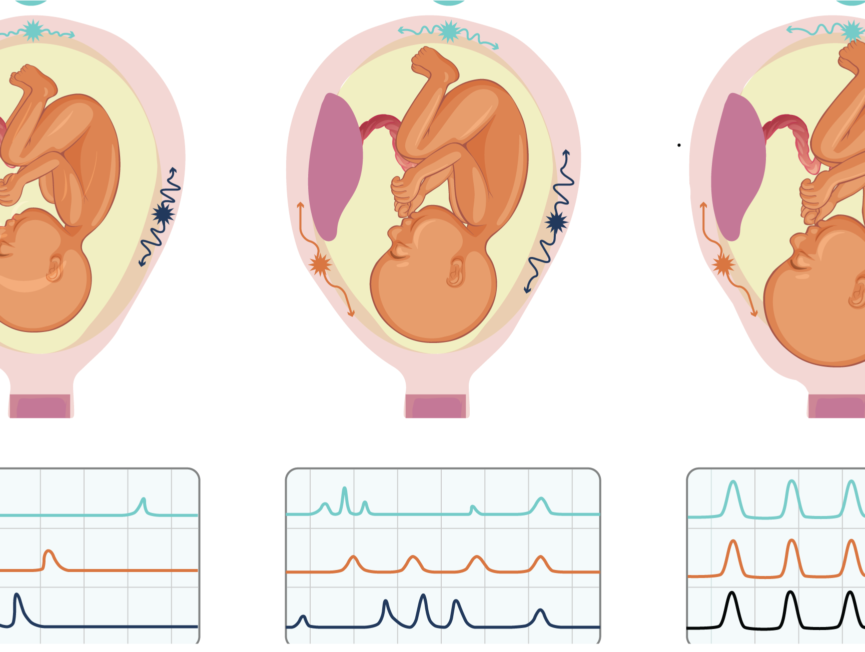 The Physiological Difference Between Braxton Hicks and Labor ...
The Physiological Difference Between Braxton Hicks and Labor .../40-5b355c25c9e77c00379a9338.png) 40 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More
40 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More Irritable Uterus: Is This Normal?
Irritable Uterus: Is This Normal? How to distinguish between false labor and actual labor pains - Quora
How to distinguish between false labor and actual labor pains - Quora How to correctly time labor contractions » home
How to correctly time labor contractions » home Braxton Hicks and Real Contractions | Beaver Dam Womens Health
Braxton Hicks and Real Contractions | Beaver Dam Womens Health Understanding and Identifying Braxton Hicks Contractions
Understanding and Identifying Braxton Hicks Contractions Irritable Uterus: Is This Normal?
Irritable Uterus: Is This Normal?/40-5b355c25c9e77c00379a9338.png) 40 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More
40 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Baby Development, and More Braxton Hicks Contractions: Recognizing Practice Labor (Infographic)
Braxton Hicks Contractions: Recognizing Practice Labor (Infographic)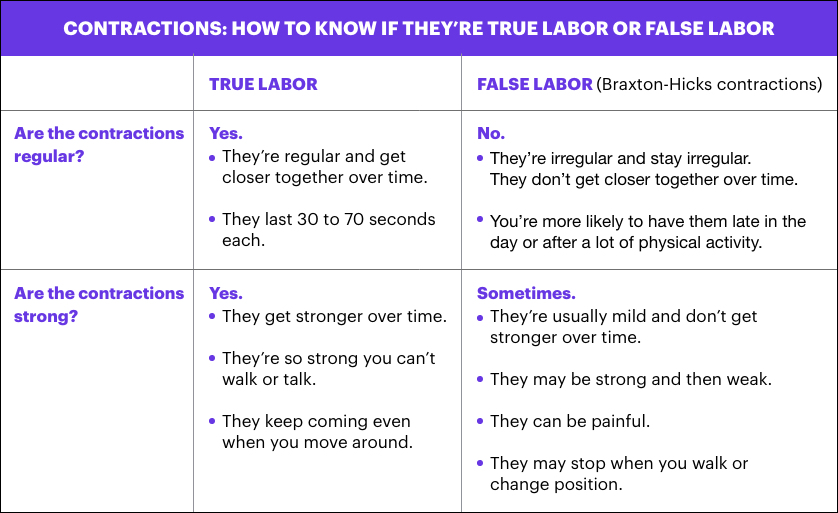 Contractions and signs of labor | March of Dimes
Contractions and signs of labor | March of Dimes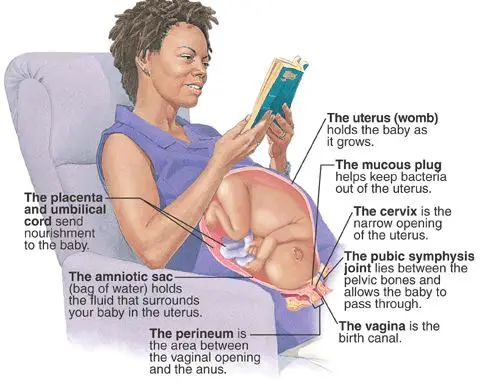 Braxton Hicks Contractions: What Are They & How They Are Felt? |
Braxton Hicks Contractions: What Are They & How They Are Felt? |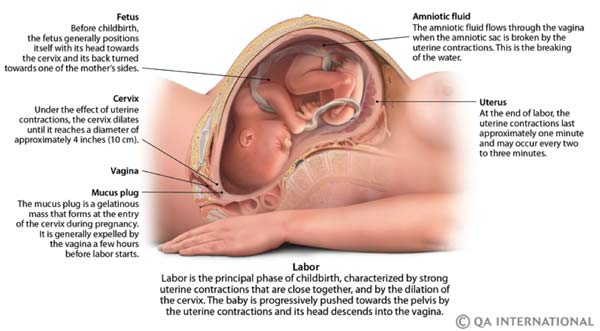 Childbirth - Visual Dictionary
Childbirth - Visual Dictionary Pitocin
Pitocin Braxton Hicks Contractions | SheCares
Braxton Hicks Contractions | SheCares Braxton Hicks and Real Contractions | Beaver Dam Womens Health
Braxton Hicks and Real Contractions | Beaver Dam Womens Health Labor Patterns - A Guide to Different Labor Patterns - Spinning Babies
Labor Patterns - A Guide to Different Labor Patterns - Spinning Babies ♥♥sATu PeRMuLaaN:::....: False labor or True Labor Contractions???
♥♥sATu PeRMuLaaN:::....: False labor or True Labor Contractions??? What do contractions feel like?
What do contractions feel like? Timing Contractions - What You Need to Know. | Bloomlife
Timing Contractions - What You Need to Know. | Bloomlife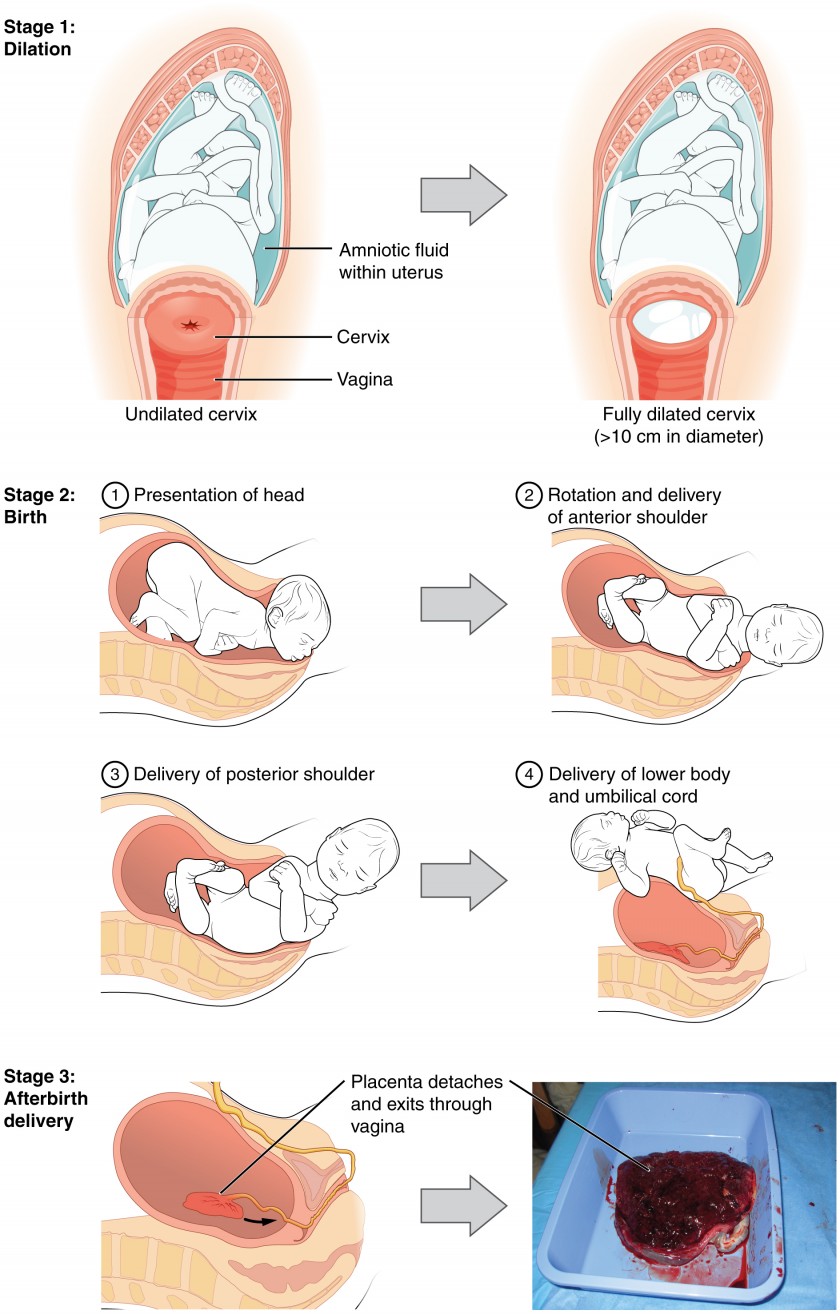 Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth | Anatomy and ...
Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth | Anatomy and ... Braxton Hicks vs. Real Contractions: How to Tell the Difference?
Braxton Hicks vs. Real Contractions: How to Tell the Difference? Labor Contractions
Labor Contractions Types of labor contractions: What do they feel like?
Types of labor contractions: What do they feel like? 9Round Fitness - Concentric vs. Eccentric Muscle Movement
9Round Fitness - Concentric vs. Eccentric Muscle Movement Prodromal Labor - American Pregnancy Association
Prodromal Labor - American Pregnancy Association Pin on Coping with early symptoms of pregnancy
Pin on Coping with early symptoms of pregnancy:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contractions-commonly-used-informal-english-1692651-v1-8415dc9952f04e08b9d5259e167e0051.png) What Are Contractions in English Grammar?
What Are Contractions in English Grammar? Solved: 8.Where Does Fertilization Typically Occur In A Hu ...
Solved: 8.Where Does Fertilization Typically Occur In A Hu ... Do Real Contractions Make It Hard To Breathe? Experts Explain How ...
Do Real Contractions Make It Hard To Breathe? Experts Explain How ... True Labor or False Labor
True Labor or False Labor Manometry tracings of the achalasia patient. Rhythmic simultaneous ...
Manometry tracings of the achalasia patient. Rhythmic simultaneous ... Solved: 47. Concentric Contractions Occur When (A) The Mus ...
Solved: 47. Concentric Contractions Occur When (A) The Mus ... Natural Mama NZ: What Childbirth Feels Like
Natural Mama NZ: What Childbirth Feels Like Contractions - Ms. Caroline's Grade 4 Website
Contractions - Ms. Caroline's Grade 4 Website Skeletal Muscle Physiology How do contractions occur? Remember ...
Skeletal Muscle Physiology How do contractions occur? Remember ... Six Types of Contractions: What to Expect Before, During, & After ...
Six Types of Contractions: What to Expect Before, During, & After ... Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby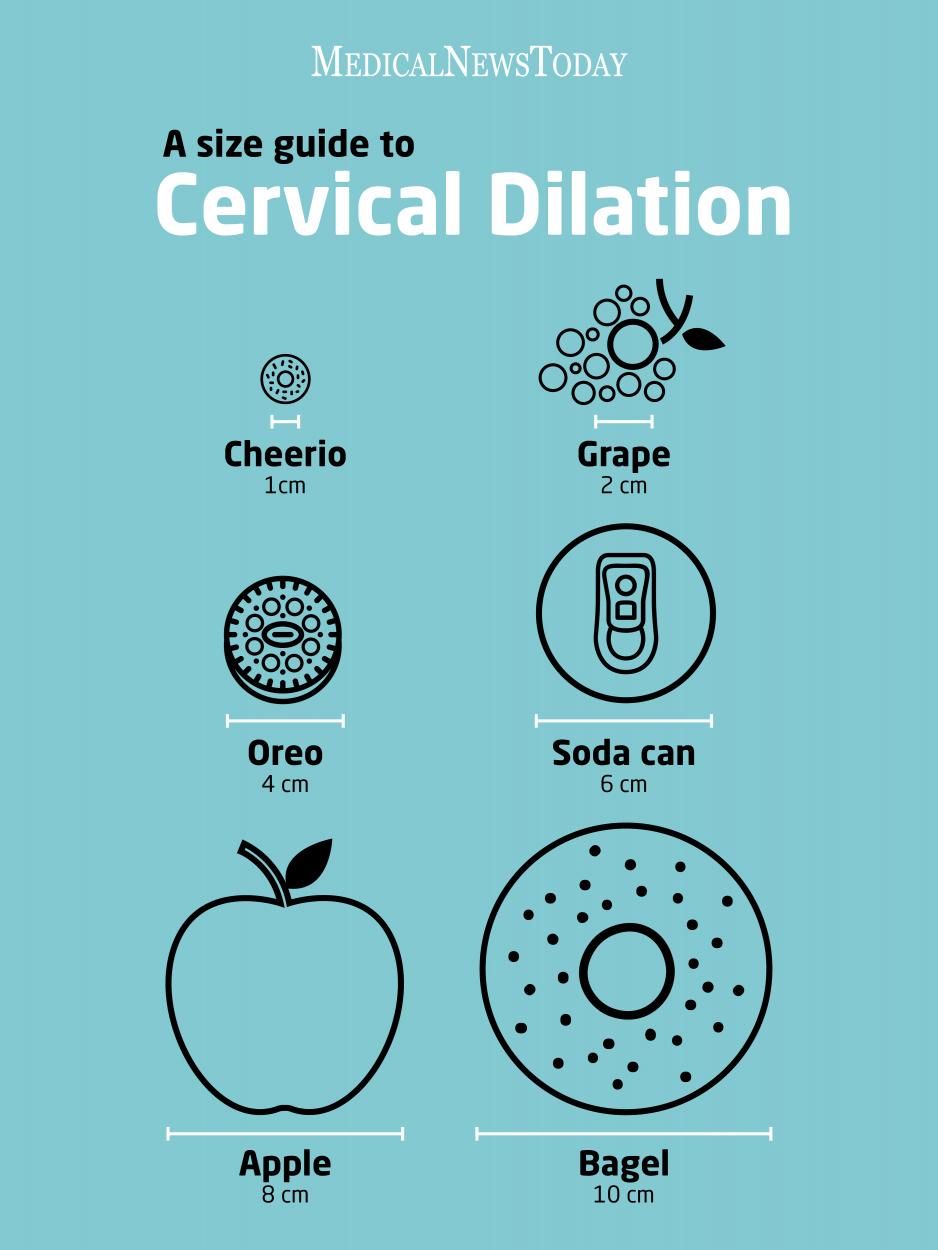 Cervix dilation chart: Stages of labor and what to expect
Cervix dilation chart: Stages of labor and what to expect French Contractions - Lawless French Lesson
French Contractions - Lawless French Lesson What causes contractions at 32 weeks pregnant? - Quora
What causes contractions at 32 weeks pregnant? - Quora Initiation OF Labor - NURSU 454 Medical Surgical Nursing I - StuDocu
Initiation OF Labor - NURSU 454 Medical Surgical Nursing I - StuDocu ST maps of pendular contractions. Pendular contractions occurring ...
ST maps of pendular contractions. Pendular contractions occurring ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar