 Woman, 36, With Fever and Malaise | Clinician Reviews
Woman, 36, With Fever and Malaise | Clinician ReviewsA miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a fetus before the 20th week of pregnancy (pregnancy loss after the 20th week are called stillbirths). Miscarriage is a natural event, not as medical or.
A miscarriage can also be called "spontaneous abortion." Other terms for the early loss of pregnancy include: ""
The doctor may also use the term symptoms of this condition is with or without vaginal bleeding. They are a sign that a miscarriage may occur.
Most miscarriages are caused by chromosomal problems that make it impossible for the baby to develop. In rare cases, these problems associated with maternal or paternal genes
Other possible causes of miscarriage may include :.
About half of all fertilized eggs die and be lost (aborted) spontaneously, usually before a woman knows she is pregnant. Among women who know they are pregnant, about 10% to 25% will have a miscarriage. Most miscarriages occur during the first seven weeks of pregnancy. The rate of miscarriage drops after the baby's heartbeat is detected
The risk of miscarriage is higher.
Possible symptoms of miscarriage may include:
During a pelvic exam, your carrier may notice that you have open (dilated) or thinned (deletion).
or may be done to check the baby's development and heart rate, and the amount of bleeding you.
The following blood tests can be done:
When a miscarriage occurs, the network passed from the vagina should be examined. This is done to determine whether it is a normal placenta, or hydatidiform mole (a rare form of growth in the uterus early pregnancy). It is also important to know if there are any pregnancy tissue remains in the uterus. In the rare cases of ectopic pregnancy can look like a miscarriage. If you have passed the network, ask your provider if the network should be sent for genetic testing. It can help to determine whether a treatable cause miscarriage present.
If the pregnancy tissue does not naturally leave the body, you probably will be closely watched to 2 weeks. Surgery () or medication may be needed to remove the remaining contents of the uterus.
After the treatment, the woman usually resume their normal menstrual cycle within 4 to 6 weeks. Any further vaginal bleeding should be carefully monitored. It is often possible to get pregnant immediately. It is suggested that you wait one normal menstrual cycle before trying to conceive again.
In rare cases, complications of miscarriage seen.
infected abortion may occur if any tissue from the placenta or the remnants of the fetus in the womb after miscarriage. Symptoms of infection include fever, vaginal bleeding does not stop, cramps and foul-smelling vaginal discharge. Infection can be serious and require immediate medical attention.
Women who lose a baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy receive different medical care. It's called or fetal death. This needs immediate medical attention.
After a miscarriage, the woman and her partner may feel sad. This is normal. If you are feeling sad not go away or get worse, seek the advice of family and friends as well as your provider. However, for some couples, history of miscarriage does not reduce the chances of having a healthy baby in the future
Please contact your provider if you :.
Earlier, complete prenatal care is the best prevention for pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage.
miscarriage caused by systemic diseases can be prevented by detecting and treating the disease before pregnancy occurs.
miscarriage are also less likely if you avoid things that are harmful to your pregnancy. These include x-rays, drugs, alcohol, high caffeine intake, and infectious diseases.
When the body of a mother having difficulty maintaining a pregnancy, signs such as vaginal bleeding slightly possible. This means there is a risk of miscarriage. But that does not mean one will definitely occur. A pregnant woman who develops signs or symptoms should contact her prenatal provider immediately.
Taking a prenatal vitamin or folic acid supplements before becoming pregnant can greatly decrease the likelihood of a miscarriage and certain birth defects.
Abortion - spontaneous; spontaneous abortion; Abortion - missed; Abortion - incomplete; Abortion - complete; Abortion - inevitable; Abortion - infected; Missed abortion; incomplete abortion; Completeabortion; Inevitable abortion; abortion infected
Catalano PM. Obesity in pregnancy. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL, et al, eds. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancy. ed 7. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017 :. Chap 41
Hobel CJ, Williams J. antepartum care. In: Hacker NF, Gambone JC, Hobel CJ, Eds. Hacker & Moore Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; , 2016: chap 7
Keyhan S, Muasher L, Muasher S. recurrent spontaneous abortion and miscarriage; etiology, diagnosis, treatment. In: Lobo RA, DM Gershenson, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. ed 7. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017 :. Chap 16
Moore KL, Persaud TVN, Torchia MG. Discussions clinically oriented problems. In: Moore KL, Persaud TVN, Torchia MG, Eds. Developing Human, The. 10 ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016 :. 503-512
Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Principles of clinical cytogenetics and genome analysis. In: Nussabaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF, Eds. Thompson & Thompson Genetics in Medicine. ed 8. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016 :. Chap 5
Reddy UM, Silver RM. Stillbirth. In: Resnick R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Mother-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. ed 8. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019: chap 45
BA Salhi, S. Nagrani acute complications of pregnancy .. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, Eds. Rosen Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018 :. Chap 178
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Fertility Center, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and A.D.A.M. the editorial team.
, For the Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC is an independent audit to verify A.D.A.M. that follows the strict standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. was among the first to achieve this important distinction for health information and services online. Learn more about A.D.A.M. and. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information.
The information provided should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of a medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other websites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsement of the other sites. Copyright 1997-2020, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.
 Management of Spontaneous Abortion - American Family Physician
Management of Spontaneous Abortion - American Family Physician The Virgin Miscarriage vs The Chad Abortion : virginvschad
The Virgin Miscarriage vs The Chad Abortion : virginvschad Miscarriages
Miscarriages Health Facts: Abortion with Pills and Spontaneous Miscarriage - NWHN
Health Facts: Abortion with Pills and Spontaneous Miscarriage - NWHN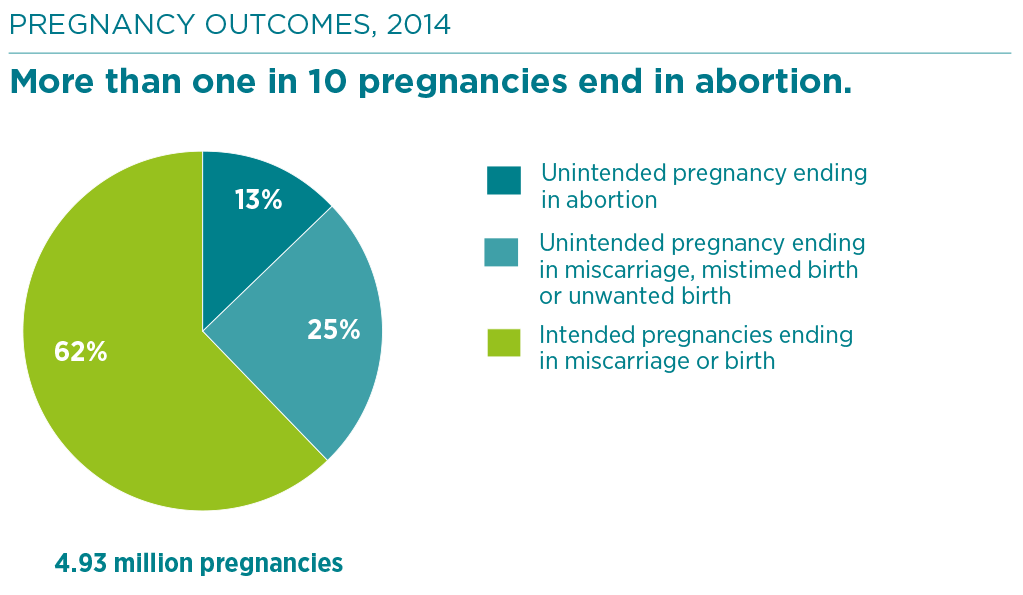 Induced Abortion and Postabortion Care in Ethiopia | Guttmacher ...
Induced Abortion and Postabortion Care in Ethiopia | Guttmacher ... Medical vs Surgical Abortion | Marie Stopes AU
Medical vs Surgical Abortion | Marie Stopes AU Percentage Who Reported Last Pregnancy that Did Not End in Live ...
Percentage Who Reported Last Pregnancy that Did Not End in Live ... Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician
Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician Abortion (miscarriage) - ppt video online download
Abortion (miscarriage) - ppt video online download Abortion and Postabortion Care in Malawi | Guttmacher Institute
Abortion and Postabortion Care in Malawi | Guttmacher Institute Modern management of miscarriage - Sagili - 2007 - The ...
Modern management of miscarriage - Sagili - 2007 - The ... Predictors of abortion/miscarriage following failure: odds ratios ...
Predictors of abortion/miscarriage following failure: odds ratios ...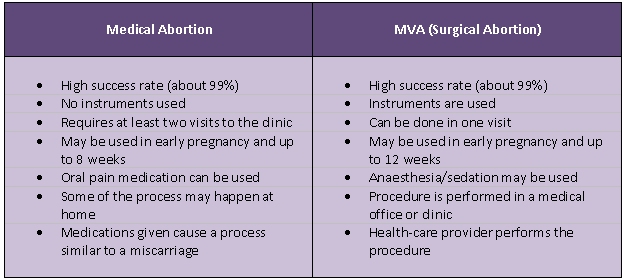 A Personal Desicion, not a Legal Debate - What is abortion?
A Personal Desicion, not a Legal Debate - What is abortion?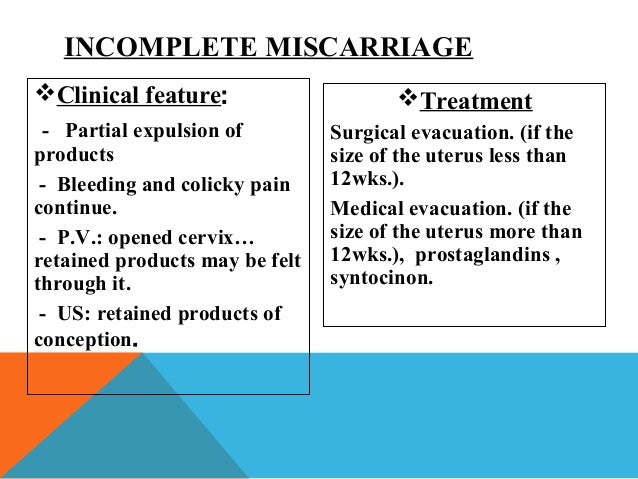 Miscarriages
Miscarriages Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician
Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician Miscarriage or abortion?' Understanding the medical language of ...
Miscarriage or abortion?' Understanding the medical language of ...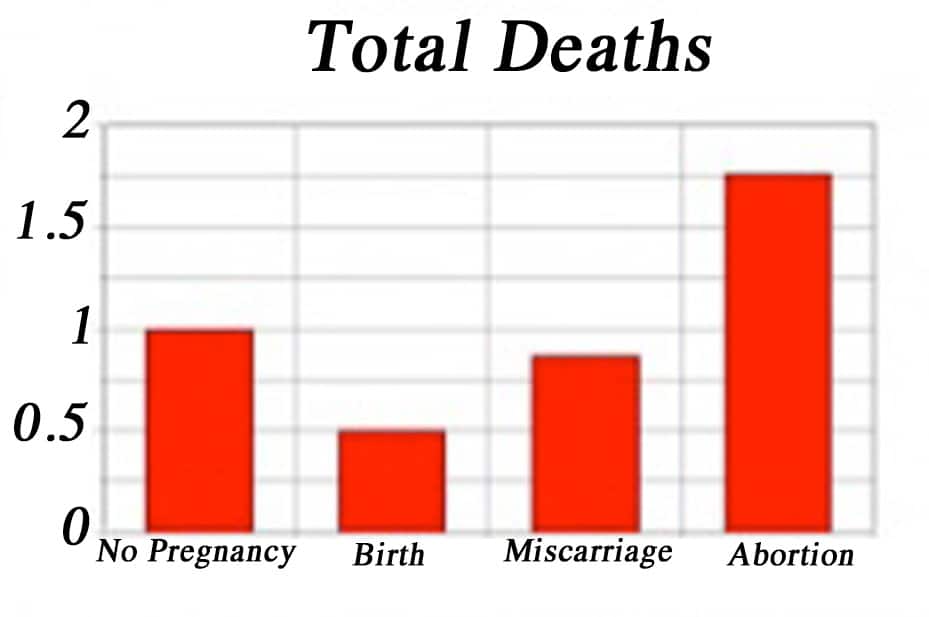 Abortion is Not Safer for Women Than Childbirth | NIFLA.org
Abortion is Not Safer for Women Than Childbirth | NIFLA.org I told them I had a miscarriage. But the nurses knew what had ...
I told them I had a miscarriage. But the nurses knew what had ... If Abortion Is Murder, Then Miscarriage Is ... | OZY
If Abortion Is Murder, Then Miscarriage Is ... | OZY Percentage Reporting Abortion/Miscarriage/Stillbirth in 1990 or ...
Percentage Reporting Abortion/Miscarriage/Stillbirth in 1990 or ... Miscarriage - Types and Definitions Threatened, Inevitable ...
Miscarriage - Types and Definitions Threatened, Inevitable ... Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion (Miscarriage)
Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion (Miscarriage) Spontaneous Miscarriages Are Explained by the Stress ...
Spontaneous Miscarriages Are Explained by the Stress ... Miscarriage
Miscarriage Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician
Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician Age and the Risk of Miscarriage | Expecting Science
Age and the Risk of Miscarriage | Expecting Science Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage ...
Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage ... Miscarriage or abortion?' Understanding the medical language of ...
Miscarriage or abortion?' Understanding the medical language of ... Bleeding during pregnancy - ppt video online download
Bleeding during pregnancy - ppt video online download Abortion and Postabortion Care in Uganda | Guttmacher Institute
Abortion and Postabortion Care in Uganda | Guttmacher Institute Question Comprehension and Recall : The Reporting of Induced ...
Question Comprehension and Recall : The Reporting of Induced ... Miscarriage Is Abortion, And Here's Why That Matters
Miscarriage Is Abortion, And Here's Why That Matters Pregnancy Outcome following a Previous Spontaneous Abortion ...
Pregnancy Outcome following a Previous Spontaneous Abortion ... Difference Between Abortion And Miscarriage - Difference Between
Difference Between Abortion And Miscarriage - Difference Between Abortion (2).ppt - Miscarriage Abortion Definition It is expulsion ...
Abortion (2).ppt - Miscarriage Abortion Definition It is expulsion ... Miscarriage - Wikipedia
Miscarriage - Wikipedia How Abortion Has Changed the Discussion of Miscarriage | Becky ...
How Abortion Has Changed the Discussion of Miscarriage | Becky ... Inevitable Abortion | Miscarriage | Remya Ranjan - YouTube
Inevitable Abortion | Miscarriage | Remya Ranjan - YouTube Pregnancy Outcome following a Previous Spontaneous Abortion ...
Pregnancy Outcome following a Previous Spontaneous Abortion ...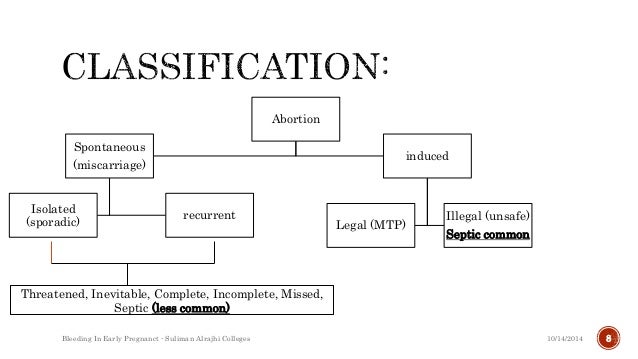 Bleeding in early pregnancy
Bleeding in early pregnancy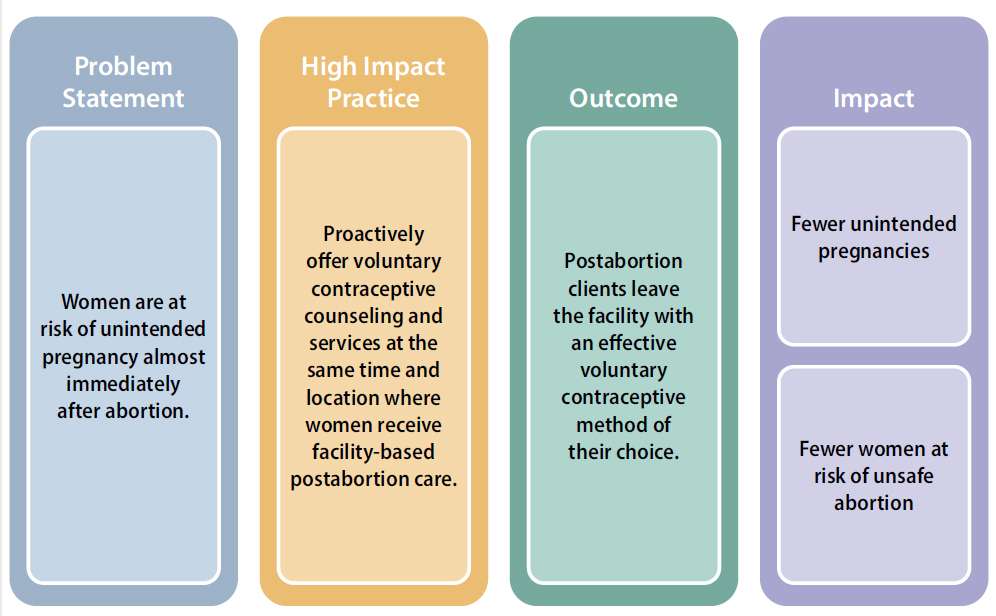 Postabortion Family Planning | HIPs
Postabortion Family Planning | HIPs Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage ...
Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage ... Pin by Sol Noya on Equality/Important society stuff | Pro choice ...
Pin by Sol Noya on Equality/Important society stuff | Pro choice ... Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician
Office Management of Early Pregnancy Loss - American Family Physician Abortion Four Times Deadlier Than Childbirth
Abortion Four Times Deadlier Than Childbirth Abortion | The A Project
Abortion | The A Project Types of Spontaneous Abortion - Threatened - Inevitable -
Types of Spontaneous Abortion - Threatened - Inevitable -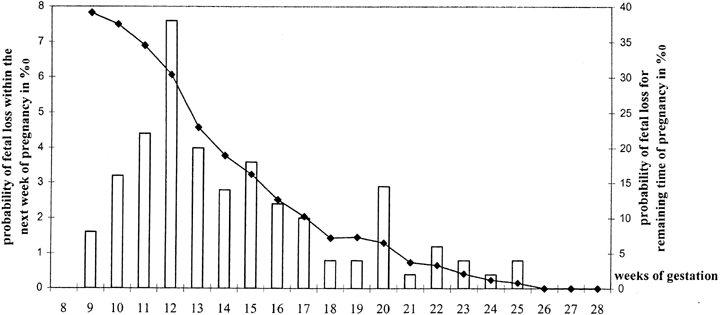 Genetic and Nongenetic Causes of Pregnancy Loss | GLOWM
Genetic and Nongenetic Causes of Pregnancy Loss | GLOWM Chromosomal abnormalities seen in early miscarriages with ...
Chromosomal abnormalities seen in early miscarriages with ... Micronized vaginal progesterone to prevent miscarriage: a critical ...
Micronized vaginal progesterone to prevent miscarriage: a critical ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar